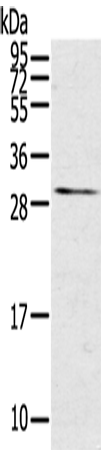

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
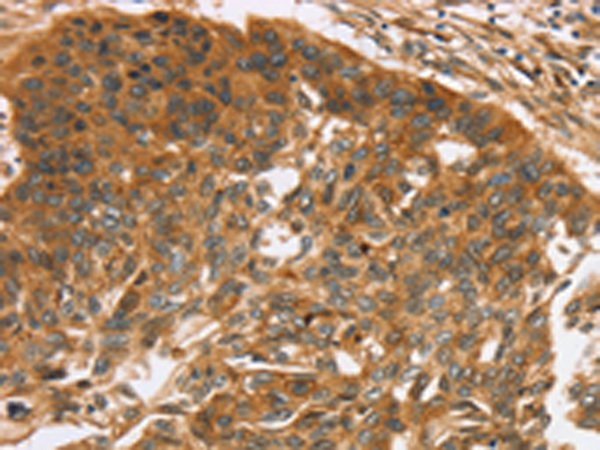
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TL1; TL1A; VEGI; VEGI192A |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNFSF15 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFSF15抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *TL1A (TNFSF15) modulates inflammatory response in experimental colitis through T cell co-stimulation*
**作者**: Meylan F, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了TNFSF15(TL1A)在结肠炎模型中的作用,发现其通过增强T细胞活化和促炎细胞因子分泌驱动炎症。开发的抗TNFSF15抗体可阻断TL1A-DR3信号,显著减轻小鼠肠道炎症,提示其治疗炎症性肠病的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *Therapeutic targeting of TNFSF15 in autoimmune diseases using a humanized monoclonal antibody*
**作者**: Shih DQ, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种人源化抗TNFSF15抗体,通过抑制TL1A与受体DR3结合,减少Th1/Th17细胞分化,在类风湿关节炎和银屑病动物模型中有效缓解病理症状,支持其作为自身免疫疾病治疗的候选药物。
3. **文献名称**: *TNFSF15 promotes antitumor immunity by modulating CD8+ T cell exhaustion in solid tumors*
**作者**: Wang X, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献发现TNFSF15在肿瘤微环境中通过调控CD8+ T细胞耗竭影响免疫应答。抗TNFSF15抗体联合PD-1抑制剂可增强抗肿瘤效果,为实体瘤免疫治疗提供了新策略。
---
以上文献均聚焦于TNFSF15抗体的功能机制及治疗应用,涵盖炎症、自身免疫病和肿瘤领域。如需具体文章链接或补充文献,可进一步提供检索关键词。
**Background of TNFSF15 Antibody**
TNFSF15 (tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 15), also known as TL1A, is a cytokine encoded by the *TNFSF15* gene. It binds to the death domain receptor DR3 (TNFRSF25) and the decoy receptor DcR3 (TNFRSF6B), playing a critical role in modulating immune responses, particularly in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. TNFSF15 is expressed by endothelial cells, monocytes, and lymphocytes, and its signaling promotes pro-inflammatory pathways, including T-cell activation, cytokine production, and angiogenesis.
Dysregulation of TNFSF15 has been implicated in pathologies such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), rheumatoid arthritis, and certain cancers. Elevated TNFSF15 levels correlate with disease severity in IBD, suggesting its role as a therapeutic target. TNFSF15 antibodies are designed to neutralize this cytokine, thereby inhibiting DR3-mediated signaling and attenuating excessive inflammation.
Preclinical and clinical studies have explored anti-TNFSF15 antibodies for treating IBD, demonstrating potential in reducing intestinal inflammation and mucosal damage. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid interference with homeostatic immune functions and addressing the dual-receptor interaction (DR3 vs. DcR3). Current research also investigates combination therapies and biomarkers to predict patient responsiveness.
Overall, TNFSF15 antibodies represent a promising therapeutic strategy for immune-mediated disorders, with ongoing efforts focused on enhancing efficacy and safety profiles.
×