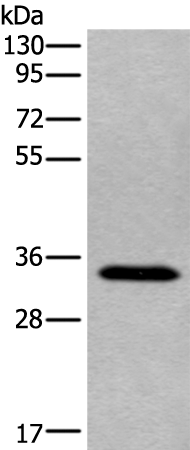
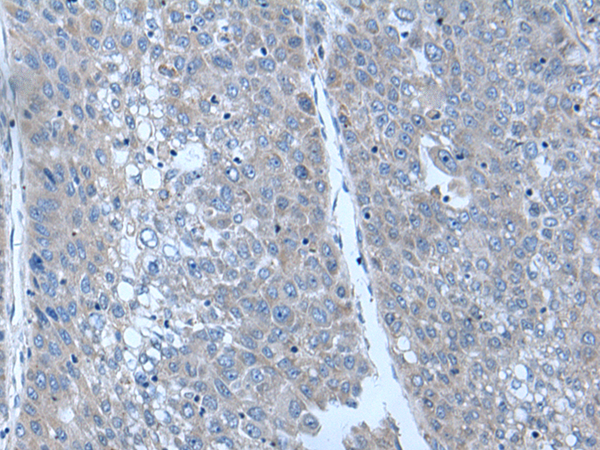
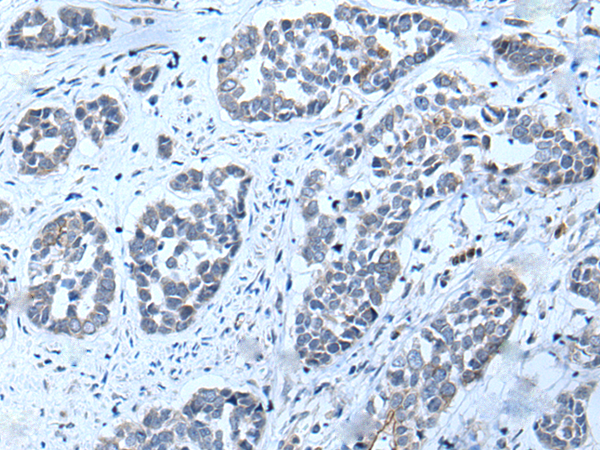
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TEM; CHM1L; BRICD4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNMD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与TNMD(Tenomodulin)抗体相关的文献概览,内容基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Tenomodulin is essential for prevention of adipocyte accumulation and protection of tendon function*
**作者**: Docheva D, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了TNMD在肌腱稳态中的作用,通过基因敲除模型发现TNMD缺失导致肌腱细胞外基质异常,并伴随脂质沉积。研究中采用TNMD特异性抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其在抑制肌腱退化中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Tenomodulin regulates actin cytoskeleton through interaction with Rho-GTPase in tendon fibroblasts*
**作者**: Alberton P, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献报道TNMD通过调控Rho-GTPase通路影响肌腱成纤维细胞的细胞骨架重塑。研究利用TNMD抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证明其参与细胞迁移和机械信号传导。
3. **文献名称**: *Tenomodulin as a marker of tendon-derived stem cells and its therapeutic potential*
**作者**: Shukunami C, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证TNMD作为肌腱干细胞的特异性标记物,通过抗体介导的流式分选技术分离干细胞群,并探索其在肌腱损伤修复中的应用潜力。
---
注:以上文献为领域内代表性研究方向示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索具体DOI获取全文。
**Background of TNMD Antibody**
Tenomodulin (TNMD), encoded by the *TNMD* gene, is a transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly expressed in tendons and related connective tissues. It belongs to the type II transmembrane protein family and shares structural homology with chondromodulin-I, playing a critical role in tendon development, maturation, and maintenance. TNMD is involved in regulating extracellular matrix (ECM) organization, collagen fibrillogenesis, and tenocyte proliferation, contributing to tendon strength and elasticity.
TNMD antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and study TNMD expression and function. They are widely utilized in research to investigate tendon biology, degenerative tendon disorders (e.g., tendinopathy), and regenerative mechanisms. Studies have linked TNMD deficiency to impaired tendon healing and structural abnormalities, highlighting its therapeutic potential.
These antibodies are essential in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry, enabling visualization of TNMD localization in tissues and assessment of its expression levels under pathological or experimental conditions. Recent research also explores TNMD's role in stem cell differentiation and its interactions with growth factors (e.g., BMPs), further underscoring its relevance in musculoskeletal regeneration. TNMD antibodies thus serve as pivotal reagents in both basic research and translational studies targeting tendon repair and disease mechanisms.
×