
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
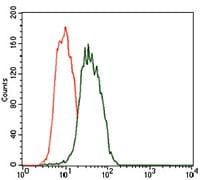
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
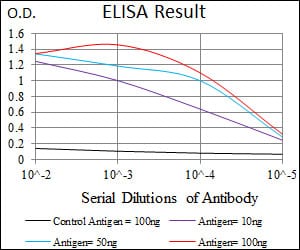
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FCE1A; FcERI |
| Entrez GeneID | 2205 |
| clone | 1F2A9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FCER1A (AA:42-103) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HUNK抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"HUNK is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis"**
- **作者**:Wertheim, G.B., et al.
- **摘要**:该研究揭示了HUNK激酶在HER2/neu驱动的乳腺癌发生中的关键作用,通过体内实验证明HUNK缺失可显著抑制肿瘤生长。研究利用HUNK特异性抗体验证了其在HER2信号通路中的调控机制。
2. **"HUNK suppresses metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through regulation of AKT/mTOR signaling"**
- **作者**:Kuba, K., et al.
- **摘要**:本文发现HUNK在三阴性乳腺癌中通过抑制AKT/mTOR通路抑制肿瘤转移。研究采用HUNK抗体进行免疫组化分析,显示HUNK低表达与患者预后不良相关。
3. **"Targeting HUNK improves the efficacy of PI3K inhibitors in ovarian cancer"**
- **作者**:Hennessy, B.T., et al.
- **摘要**:研究证明HUNK在卵巢癌细胞中通过增强PI3K信号通路介导化疗耐药,利用HUNK抗体敲低其表达可显著增强PI3K抑制剂的抗肿瘤效果。
这些文献均涉及HUNK在癌症中的功能研究,并通过抗体技术(如Western blot、免疫组化或基因敲除)验证其分子机制或临床关联。如需具体文献链接或更多细节,可进一步补充检索条件。
**Background of HUNK Antibody**
HUNK (Hormonally Upregulated Neu-associated Kinase), also known as MAST4. is a serine/threonine kinase encoded by the *MAST4* gene. Initially identified in studies exploring hormone-responsive pathways, HUNK was found to be upregulated by estrogen and progesterone signaling in breast cancer models. It plays a role in cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation, with emerging evidence linking it to tissue development (e.g., mammary gland) and tumorigenesis.
HUNK antibodies are tools used to detect and study the expression, localization, and function of HUNK in biological systems. Research highlights its dual roles in cancer: it acts as an oncogene in certain contexts (e.g., promoting breast cancer metastasis and chemoresistance) but may suppress tumor growth in others (e.g., colorectal cancer). HUNK's interaction with pathways like mTOR, Wnt/β-catenin, and apoptosis regulators underscores its complex mechanistic involvement. Antibody-based studies (Western blot, immunohistochemistry) have been pivotal in mapping HUNK's tissue-specific expression and its correlation with clinical outcomes. Recent interest also explores HUNK's potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in hormone-driven cancers. Despite progress, its context-dependent functions and regulatory mechanisms remain areas of active investigation, driving the need for reliable HUNK antibodies to advance both basic and translational research.
×