| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
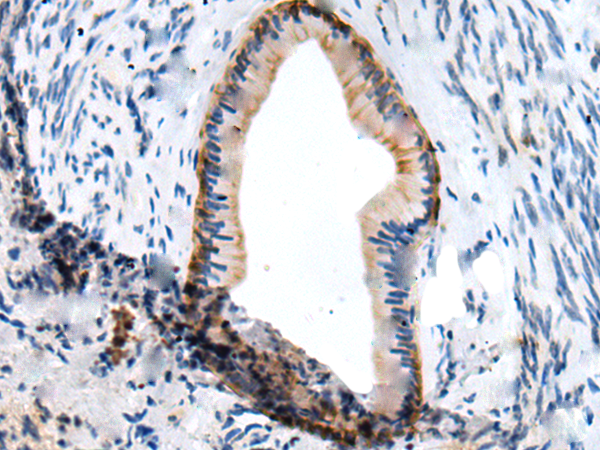
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GP; JI; TN; HXB; GMEM; TN-C; DFNA56; 150-225 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于TNC(Tenascin-C)抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究整理,非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting Tenascin-C with a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Inhibits Tumor Growth in Glioblastoma Models*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向TNC的新型单克隆抗体,通过抑制TNC与肿瘤微环境中的整合素相互作用,显著抑制胶质母细胞瘤小鼠模型的肿瘤生长和血管生成。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Tenascin-C as a Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Diagnostic Potential of Anti-TNC Antibody-Based Imaging*
**作者**:Lee S, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了TNC抗体在结直肠癌分子成像中的应用,证明其能够特异性识别肿瘤组织中的TNC高表达区域,为无创诊断和术中导航提供潜在工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-Tenascin-C Antibody Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis via Modulation of Macrophage Polarization*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,靶向TNC的抗体可通过调节巨噬细胞从促纤维化M2型向抗炎M1型转化,减轻小鼠肺纤维化模型的病理进展,为治疗纤维化疾病提供新策略。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“Tenascin-C antibody”或“anti-TNC antibody”获取最新研究。
Tenascin-C (TNC) is a large extracellular matrix glycoprotein involved in tissue development, inflammation, and cancer progression. It is transiently expressed during embryogenesis but re-emerges in pathological conditions, including wound healing, fibrosis, and tumorigenesis. TNC interacts with cell surface receptors (e.g., integrins, TLR4) and other ECM components, modulating cell adhesion, migration, and signaling pathways. Its dynamic expression and structural complexity (e.g., multiple splice variants) make it a biomarker and therapeutic target.
TNC antibodies are tools to detect TNC expression in tissues or biological fluids, aiding research and clinical diagnostics. In cancer, elevated TNC correlates with metastasis, angiogenesis, and poor prognosis, driving interest in therapeutic antibodies. For example, monoclonal antibodies like F16 (targeting TNC’s A1 domain) have been explored for tumor-targeted drug delivery or radioimmunotherapy. Additionally, autoimmune responses against TNC have been linked to chronic inflammatory diseases, where autoantibodies may serve as diagnostic markers.
Challenges include TNC’s structural heterogeneity and context-dependent roles, requiring antibody specificity validation. Advances in antibody engineering (e.g., humanized or bispecific formats) aim to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Overall, TNC antibodies bridge mechanistic studies and translational applications, offering insights into disease mechanisms and potential treatment strategies.
×