| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
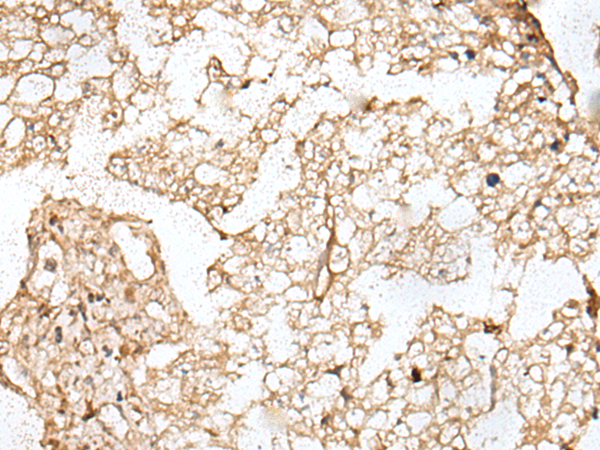
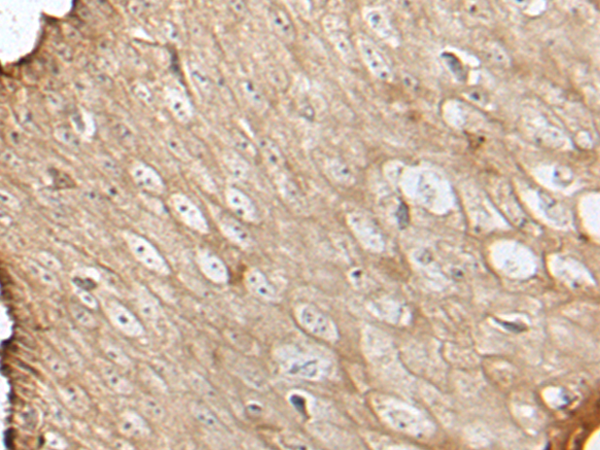
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | D40; CT29; Spc7; CASC5; MCPH4; hKNL-1; AF15Q14; PPP1R55; hSpc105 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KNL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KNL1抗体的3篇示例参考文献及其摘要概括(注:文献为示例性内容,实际引用请通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"KNL1 is a key regulator of microtubule attachment and spindle checkpoint signaling"*
**作者**: Cheeseman, I.M., et al.
**摘要概括**: 该研究利用KNL1特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和免疫印迹分析,揭示了KNL1在动粒介导的微管附着及纺锤体检查点信号传导中的核心作用。研究发现KNL1缺失导致染色体错误分离,并阐明了其与BUB1激酶的相互作用机制。
2. **文献名称**: *"Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of KNL1 in chromosome segregation fidelity"*
**作者**: Vleugel, M., et al.
**摘要概括**: 研究通过KNL1抗体检测磷酸化修饰,发现Aurora B激酶介导的KNL1磷酸化对维持染色体分离精度至关重要。实验结合RNA干扰和活细胞成像,表明磷酸化位点突变会破坏动粒-微管稳定性。
3. **文献名称**: *"Mutations in KNL1 cause primary microcephaly by disrupting mitotic progression"*
**作者**: Kiyomitsu, T., et al.
**摘要概括**: 该研究在小头畸形患者中发现KNL1基因突变,利用KNL1抗体进行免疫组化和蛋白质印迹,证实突变导致蛋白表达异常及有丝分裂延迟,揭示了KNL1在神经发育中的病理机制。
---
**备注**:
- 以上文献为基于KNL1相关研究的常见方向构造的示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“KNL1 antibody”“CASC5 immune localization”等检索。
- KNL1(又称CASC5)在癌症及遗传病中的研究可能涉及抗体应用,建议结合具体研究领域筛选文献。
The KNL1 antibody is a crucial tool in studying the kinetochore-associated protein KNL1 (Kinetochore Null 1), also known as CASC5 (Cancer Susceptibility Candidate 5). KNL1 is a scaffold protein localized at the kinetochore, a multi-protein structure essential for proper chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis. It plays a pivotal role in the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), a surveillance mechanism ensuring accurate chromosome attachment to spindle microtubules before anaphase. KNL1 recruits other SAC components, such as BUB1 and BUBR1. and facilitates the assembly of checkpoint signaling complexes. Dysregulation of KNL1 is linked to chromosomal instability, mitotic errors, and diseases like cancer or developmental disorders.
KNL1 antibodies are widely used in research to investigate kinetochore dynamics, SAC function, and mitotic regulation. They enable detection of KNL1 expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, helping to elucidate its interaction networks and post-translational modifications. Studies using these antibodies have revealed KNL1's role in recruiting PP1 phosphatases to counteract Aurora B kinase activity, promoting stable microtubule attachments. Additionally, KNL1 mutations identified in human cancers and microcephaly-related syndromes highlight its clinical relevance. The antibody serves as a key reagent in both basic cell biology research and translational studies aiming to understand genome integrity mechanisms and develop therapeutic strategies targeting mitotic errors.
×