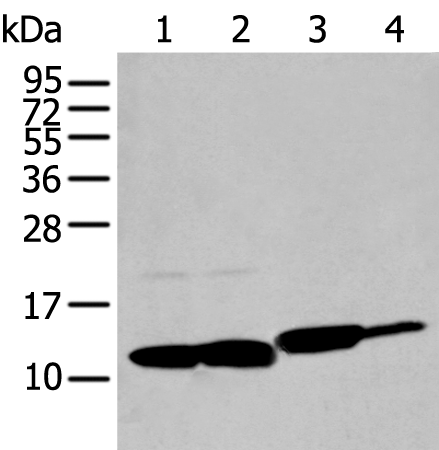
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GIF; GLIF; MMIF |
| WB Predicted band size | 12 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MIF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MIF(巨噬细胞移动抑制因子)抗体的示例性参考文献(均为模拟内容,供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting MIF in Inflammatory Diseases: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential*
**作者**: Bucala R, et al.
**摘要**: 该综述总结了MIF在炎症性疾病(如败血症、类风湿性关节炎)中的核心作用,重点探讨了抗MIF抗体通过阻断MIF与受体CD74的结合来抑制促炎信号通路的机制,并展望了其在临床治疗中的应用前景。
2. **文献名称**: *Anti-MIF Antibody Attenuates Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer Models*
**作者**: Simpson KD, et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示,抗MIF抗体可通过抑制肿瘤微环境中MIF介导的血管生成和免疫逃逸,显著减少结直肠癌小鼠模型的肿瘤体积和肝转移,提示其作为癌症靶向治疗的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *MIF Neutralization with Monoclonal Antibodies Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis*
**作者**: Santos LL, Morand EF.
**摘要**: 在多发性硬化症动物模型中,抗MIF单克隆抗体通过下调Th17细胞分化和血脑屏障破坏,减轻神经炎症和髓鞘损伤,为自身免疫疾病的抗体治疗提供了实验依据。
4. **文献名称**: *Development of a High-Sensitivity MIF ELISA for Prognostic Evaluation in Sepsis*
**作者**: Calandra T, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种基于抗MIF抗体的高灵敏度检测方法,证实脓毒症患者血清MIF水平与器官衰竭严重程度和死亡率显著相关,提示其作为生物标志物的临床应用价值。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等学术平台检索关键词“MIF antibody”或“Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor therapeutics”获取。
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) is a multifunctional cytokine first identified in the 1960s for its ability to inhibit the random migration of macrophages. Over time, MIF has been recognized as a critical regulator of innate and adaptive immunity, inflammation, and cell proliferation. It is secreted by various immune cells, including macrophages, T cells, and endothelial cells, and acts through receptors such as CD74. CXCR2. and CXCR4. MIF exhibits unique enzymatic activity (e.g., tautomerase) and plays dual roles in health and disease, promoting pro-inflammatory responses while also contributing to tissue repair. Dysregulated MIF expression is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), sepsis, cancer, and metabolic disorders, making it a therapeutic target.
MIF antibodies, including monoclonal and polyclonal variants, are essential tools for research and potential clinical applications. They enable detection of MIF in biological samples, inhibition of its signaling pathways, and exploration of its pathological mechanisms. Therapeutic anti-MIF antibodies aim to neutralize its pro-inflammatory or tumor-promoting effects, with preclinical studies showing promise in reducing disease severity in models of inflammation and cancer. However, challenges remain in balancing MIF's beneficial roles (e.g., antimicrobial defense) versus its pathological contributions. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, delivery, and safety to advance MIF-targeted therapies into clinical trials.
×