| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
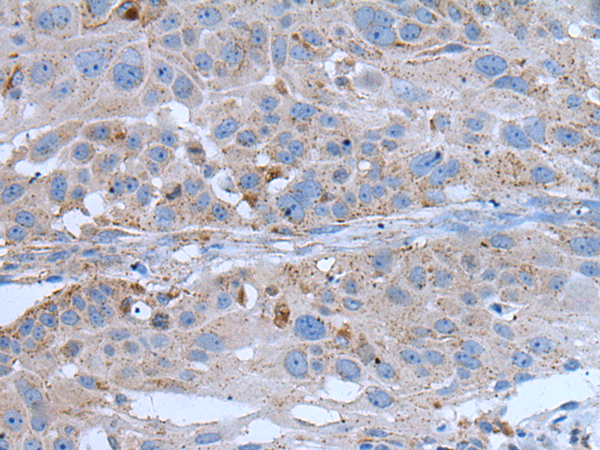
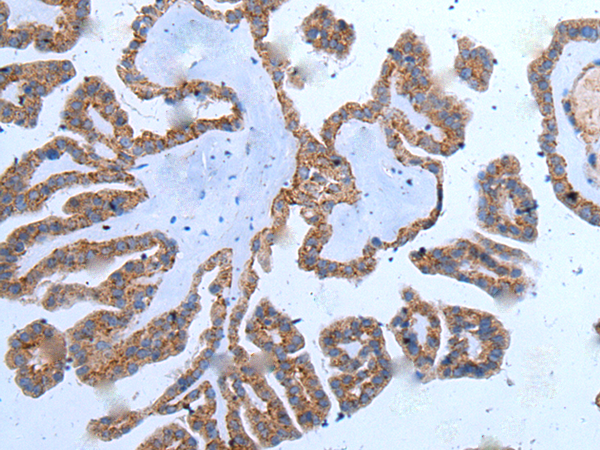
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human YPEL4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于YPEL4抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其功能及应用的简要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**: *YPEL4 regulates mitochondrial apoptosis and actin polymerization in cancer cells*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过YPEL4抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现YPEL4通过调控线粒体凋亡通路抑制肿瘤生长,并影响细胞骨架重塑。抗体被用于验证不同癌细胞系中YPEL4的蛋白表达水平。
---
2. **文献名称**: *The role of YPEL4 in cellular senescence and aging-related diseases*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 本文利用YPEL4抗体开展免疫组化分析,发现YPEL4在衰老细胞中表达显著上调,可能通过p53通路诱导细胞周期停滞。抗体帮助证实其在衰老组织中的定位及功能关联。
---
3. **文献名称**: *YPEL4 interacts with Hippo signaling components to modulate organ size*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用YPEL4抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)实验,揭示YPEL4与Hippo通路蛋白相互作用,调控器官发育大小。抗体特异性验证为关键实验步骤,支持其在哺乳动物模型中的功能机制解析。
---
注:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新研究,结合具体实验需求筛选文献。
The YPEL4 antibody is a tool used to study the YPEL4 protein, a member of the Yippee-like (YPEL) family implicated in cell cycle regulation and cellular senescence. YPEL4. encoded by the YPEL4 gene, is evolutionarily conserved and shares homology with Drosophila Yippee, a protein involved in mitosis and metal ion binding. Human YPEL4 is localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm, where it participates in cell proliferation control and stress response pathways. Studies suggest YPEL4 overexpression induces cellular senescence, while its downregulation is linked to tumorigenesis in certain cancers, highlighting its potential role as a tumor suppressor.
YPEL4 antibodies, typically polyclonal or monoclonal, are designed to detect endogenous YPEL4 protein levels in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies are critical for elucidating YPEL4's molecular mechanisms, including its interaction with cell cycle regulators (e.g., p21. p53) and involvement in aging-related pathways. Commercial YPEL4 antibodies are often validated using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to ensure specificity. Research utilizing these reagents has explored YPEL4's dysregulation in cancers, such as breast and colorectal cancer, where its expression correlates with clinical outcomes. Ongoing studies aim to clarify YPEL4's dual roles in senescence and cancer, positioning it as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target.
×