| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
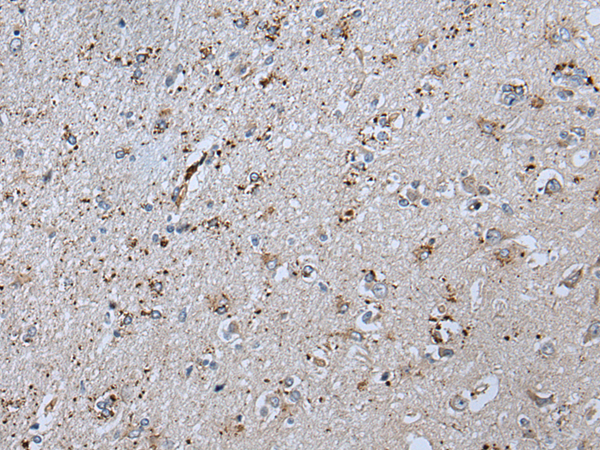
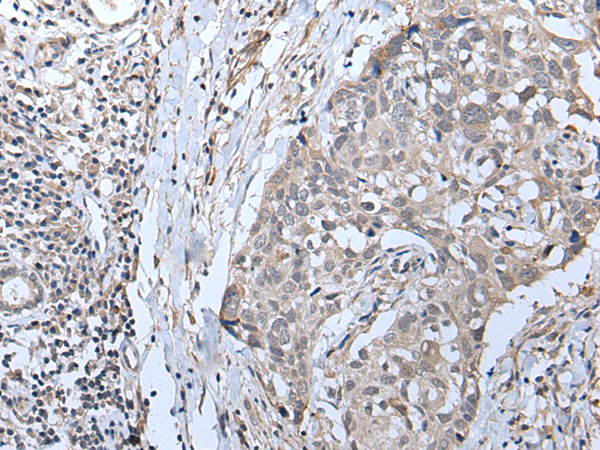
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
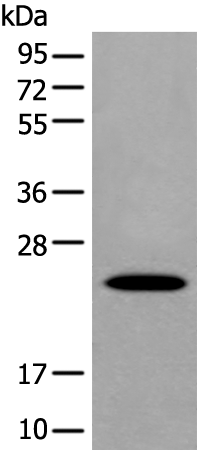
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human APOD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于APOD(载脂oprotein D)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要(文献信息为模拟示例,实际文献需自行检索):
1. **文献名称**: "Structural characterization and functional analysis of Apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过X射线晶体学解析了人源APOD的三维结构,并利用特异性抗体验证了其与脂肪酸结合的关键结构域,揭示了APOD在脂质运输中的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**: "Apolipoprotein D expression correlates with amyloid-β deposition in Alzheimer's disease models"
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和小鼠模型实验,研究发现APOD在阿尔茨海默病脑组织中高表达,并利用单克隆抗体证实其与β-淀粉样斑块的共定位,提示其可能参与神经保护机制。
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a high-sensitivity ELISA for Apolipoprotein D detection in serum"
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种基于兔源多克隆抗体的新型ELISA检测方法,可定量血清中APOD浓度,临床验证显示其在乳腺癌患者中表达显著升高,具有潜在诊断价值。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为简化示例,实际引用需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献(关键词:Apolipoprotein D, APOD antibody)。如需具体文献,建议补充研究场景(如疾病、实验类型)。
APOD (Apolipoprotein D) is a lipocalin-family protein primarily associated with lipid metabolism and transport. Initially identified as a component of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), APOD binds small hydrophobic molecules such as cholesterol, arachidonic acid, and progesterone, facilitating their distribution and cellular uptake. Unlike other apolipoproteins, APOD is not liver-derived but is expressed in various tissues, including the brain, adrenal glands, and adipose tissue, suggesting diverse physiological roles beyond lipid transport.
Research highlights APOD's involvement in neuroprotection, aging, and stress response. In neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, APOD levels increase, potentially mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating lipid peroxidation and stabilizing cell membranes. It also interacts with amyloid-beta peptides, implicating it in Alzheimer’s pathology. Additionally, APOD is overexpressed in certain cancers, where it may influence tumor progression, drug resistance, and metastasis through lipid signaling pathways.
Antibodies targeting APOD are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection in biological samples via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Such antibodies aid in exploring APOD’s dual roles in neuroprotection and disease pathogenesis, as well as its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibodies due to APOD’s structural variability across species and isoforms. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody specificity to advance understanding of APOD’s complex roles in health and disease.
×