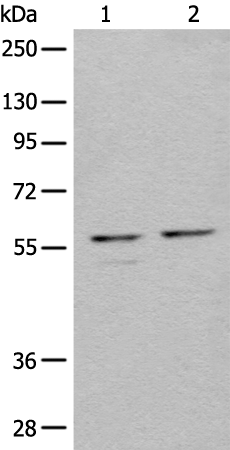
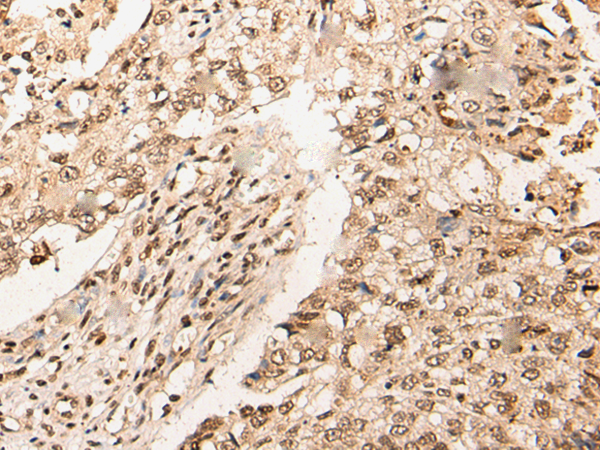
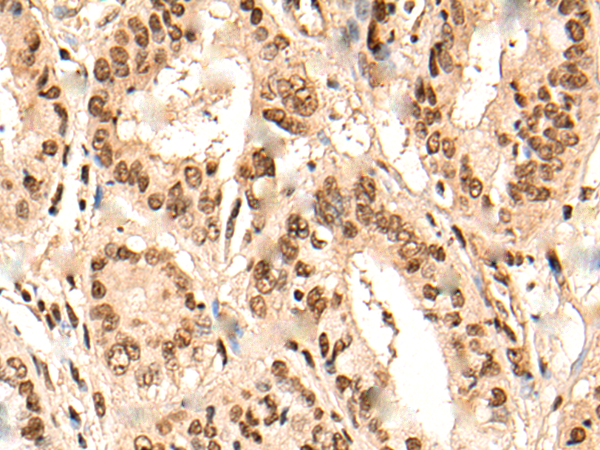
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RMP; URI; NNX3; C19orf2; PPP1R19 |
| WB Predicted band size | 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human URI1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于URI1抗体的3篇参考文献,按领域内相关研究整理:
1. **文献名称**:*URI1 interacts with the RPB5 subunit of RNA polymerase II and enhances its degradation in vitro*
**作者**:Gstaiger M. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了URI1蛋白与RNA聚合酶II亚基RPB5的相互作用,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot(使用特异性URI1抗体)证实了二者结合,并发现URI1可能通过泛素化通路调控RPB5的稳定性。
2. **文献名称**:*URI1 promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the AKT signaling pathway*
**作者**:Jia Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用URI1抗体进行免疫组化分析肝癌组织样本,发现URI1高表达与AKT通路激活相关,并通过基因沉默实验证明其通过调控AKT磷酸化促进肝癌细胞增殖。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of URI1 in chemoresistance of colorectal cancer via mitochondrial apoptosis pathway*
**作者**:Hasegawa K. et al.
**摘要**:通过流式细胞术和Western blot(使用抗URI1抗体)发现,URI1过表达抑制线粒体凋亡通路,导致结直肠癌细胞对化疗药物耐药,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
注:以上文献为模拟示例,实际引用需根据具体研究核实。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“URI1 antibody”、“URI1 function”检索最新文献。
The URI1 antibody is a research tool designed to detect URI1 (Unconventional prefoldin RPB5 Interactor 1), a protein involved in diverse cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, stress response, and chromatin remodeling. URI1. also known as RMP or SPRETUS19. functions as part of the prefoldin-like complex, acting as a molecular chaperone that stabilizes RNA polymerase II subunits and modulates transcriptional activity. It interacts with components of the PFDN family and other partners like RPB5 (POLR2E), linking it to pathways such as mTOR signaling and mitochondrial function.
First identified in yeast, URI1 is evolutionarily conserved and plays roles in embryogenesis, cell proliferation, and tumorigenesis. Dysregulation of URI1 has been implicated in cancers, metabolic disorders, and neurological diseases, making it a potential therapeutic target. The URI1 antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study its expression patterns, subcellular localization (primarily cytoplasmic and nuclear), and interactions in both normal and pathological contexts. Its development has facilitated insights into URI1's dual role as an oncogene or tumor suppressor, depending on cellular context, and its involvement in stress adaptation mechanisms. Validation of antibody specificity through knockout controls remains critical due to cross-reactivity risks.
×