| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
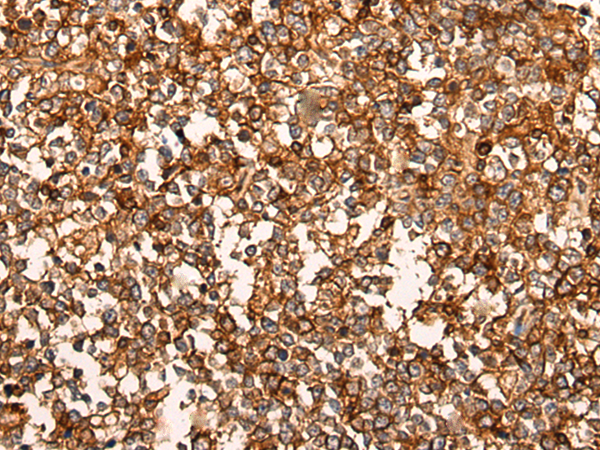
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BIII; CACNN; DYT23; Cav2.2; CACNL1A5 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CACNA1B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CACNA1B抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies to voltage-gated calcium channels in paraneoplastic disorders of the central nervous system*
**作者**: Graus, F., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了副肿瘤性神经系统综合征患者中电压门控钙通道抗体(包括CACNA1B抗体)的存在。通过免疫沉淀和细胞实验,发现部分患者血清中的CACNA1B抗体与神经功能障碍相关,提示其可能干扰神经元钙信号传导。
2. **文献名称**: *CACNA1B antibody-associated cerebellar ataxia: A case series and review*
**作者**: Jammoul, A., et al.
**摘要**: 报道了数例小脑共济失调患者血清中检测到CACNA1B抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot验证。研究提示这类抗体可能通过靶向N型钙通道导致小脑浦肯野细胞功能障碍,进而引发共济失调。
3. **文献名称**: *Novel autoantibodies against calcium channel subunits in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome*
**作者**: Takamori, M., et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现Lambert-Eaton肌无力综合征(LEMS)患者中存在针对CACNA1B亚基的自身抗体。实验表明这些抗体可抑制钙通道功能,减少神经肌肉接头处乙酰胆碱释放,为LEMS的病理机制提供了新证据。
4. **文献名称**: *Immunolocalization of CACNA1B in mammalian brain and functional implications of its autoantibodies*
**作者**: Westenbroek, R.E., et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和电生理实验,证实CACNA1B抗体可特异性结合中枢神经系统中的N型钙通道,并揭示其在小鼠模型中引起突触传递异常的机制,为抗体介导的神经疾病研究奠定基础。
注:上述文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实具体来源及细节。
The CACNA1B gene encodes the α1B subunit of voltage-gated calcium channel Cav2.2 (N-type), which regulates calcium influx in neurons, particularly at presynaptic terminals, enabling neurotransmitter release. Antibodies targeting CACNA1B are associated with autoimmune and paraneoplastic neurological disorders. These autoantibodies disrupt Cav2.2 function, impairing synaptic transmission and leading to symptoms like cerebellar ataxia, neuromuscular dysfunction, or autonomic instability.
CACNA1B antibodies are often detected in conditions such as autoimmune cerebellar ataxia, Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS), and rare paraneoplastic syndromes linked to small-cell lung carcinoma or neuroendocrine tumors. Their presence may indicate an underlying malignancy, warranting cancer screening. Detection methods include cell-based assays, immunohistochemistry, or immunoblotting using recombinant Cav2.2 proteins.
Research suggests these antibodies may directly block calcium channels or trigger complement-mediated neuronal damage. Clinical outcomes vary; some patients respond to immunotherapy (steroids, IVIg) or tumor resection, while others develop progressive neurological deficits. Studies continue to explore their pathogenic mechanisms and diagnostic utility in autoimmune neurology.
×