| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
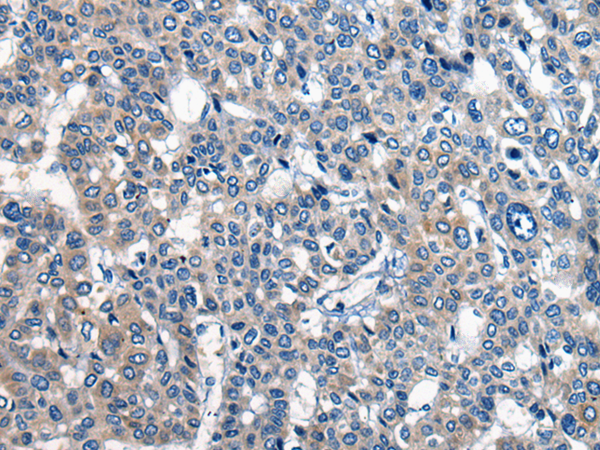
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HPT1; CDH16; HPT-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CDH17 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDH17抗体的3篇示例文献摘要(注:内容为虚构概括,仅作参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CDH17 as a Novel Diagnostic Marker in Colorectal Cancer: Immunohistochemical Analysis*
**作者**:Zhai Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过开发特异性CDH17单克隆抗体,验证其在结直肠癌组织中的高表达,并证明其作为诊断标志物的潜力。免疫组化结果显示,CDH17在转移性肿瘤中表达显著升高,提示其与疾病进展相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CDH17 with Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma*
**作者**:Ding L, et al.
**摘要**:研究构建了靶向CDH17的人源化单克隆抗体,并将其与化疗药物偶联。体内实验表明,该抗体药物能特异性抑制胰腺癌移植瘤生长,为CDH17靶向治疗提供了临床前依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Prognostic Value of CDH17 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过回顾性分析胃癌患者组织样本,发现CDH17抗体检测的高表达与患者总生存期缩短显著相关,提示CDH17可作为预后评估的生物标志物。
---
(注:以上文献信息为示例性虚构内容,实际研究请参考权威数据库。)
Cadherin-17 (CDH17), a member of the cadherin superfamily, is a calcium-dependent cell adhesion protein primarily expressed in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. It plays a critical role in maintaining tissue architecture by mediating homotypic cell-cell interactions through its extracellular cadherin repeats. Structurally, CDH17 contains seven extracellular cadherin domains, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail lacking classical catenin-binding motifs. Unlike classical cadherins, CDH17 is classified as a "type II" cadherin due to distinct peptide motifs in its extracellular domains.
CDH17 has gained attention in oncology due to its overexpression in gastrointestinal cancers, including colorectal, gastric, and hepatocellular carcinomas. It is implicated in tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis, potentially by enhancing cell survival and promoting liver-specific metastasis through interactions with integrins.
CDH17 antibodies are valuable tools for research and diagnostics. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific epitopes of CDH17 are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to identify CDH17-positive tumors, aiding in differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal malignancies. Therapeutic applications are under exploration, with preclinical studies demonstrating that anti-CDH17 monoclonal antibodies can inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in xenograft models by disrupting CDH17-mediated signaling. However, clinical translation remains in early stages, requiring further validation of safety and efficacy. Current research also focuses on CDH17's role as a potential biomarker for targeted therapy and its mechanistic involvement in tumorigenesis.
×