| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
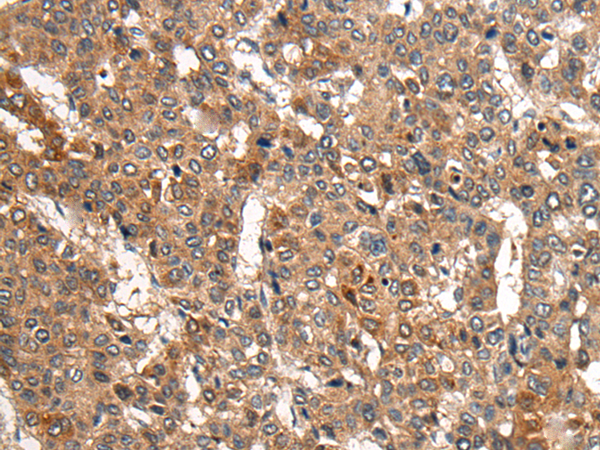
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | USH1D; CDHR23 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CDH23 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDH23抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其应用和功能研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CDH23 mutations and phenotype in Usher syndrome type 1D*
**作者**:Bork JM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化技术,利用CDH23特异性抗体定位其在人类耳蜗组织中的表达,揭示了CDH23基因突变导致Usher综合征1D型的分子机制,证实抗体在蛋白功能缺失分析中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The tip-link antigen, a protein associated with the transduction complex of sensory hair cells, is protocadherin-15*
**作者**:Ahmed ZM, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用CDH23抗体与protocadherin-15抗体共定位实验,证明两者在内耳毛细胞静纤毛尖端形成复合物,支持CDH23在听觉信号转导中的结构作用,抗体用于验证蛋白相互作用及组织分布。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Cadherin 23 and protocadherin 15 interact to form tip-link filaments in sensory hair cells*
**作者**:Siemens J, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,研究验证了CDH23抗体的特异性,并揭示CDH23与protocadherin-15共同构成毛细胞尖端连接丝,对抗体在解析耳蜗机械转导机制中的应用进行了系统评价。
---
以上文献展示了CDH23抗体在定位、蛋白互作及疾病机制研究中的关键作用,适用于耳聋和细胞粘附相关领域。
CDH23 (Cadherin-23) is a calcium-dependent transmembrane protein belonging to the cadherin superfamily, which plays critical roles in cell-cell adhesion and mechanosensory signaling. It is particularly vital in the inner ear, where it contributes to the formation of tip links between stereocilia of hair cells, essential for converting sound-induced mechanical vibrations into electrical signals. Mutations in the CDH23 gene are linked to Usher syndrome type 1D (USH1D) and non-syndromic hereditary deafness (DFNB12), highlighting its importance in auditory function. In the retina, CDH23 is involved in photoreceptor cell maintenance, further connecting it to USH1D-associated vision loss.
CDH23 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both auditory and visual systems. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, aiding research on cochlear development, hair cell organization, and disease mechanisms. CDH23's large extracellular domain, containing multiple cadherin repeats, poses challenges for antibody development, requiring careful epitope selection. Commercial CDH23 antibodies are often validated in specific tissues (e.g., mouse inner ear) and applications, necessitating thorough verification for experimental models. Their use extends to diagnostic research, particularly in characterizing genetic hearing loss and Usher syndrome pathologies.
×