| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
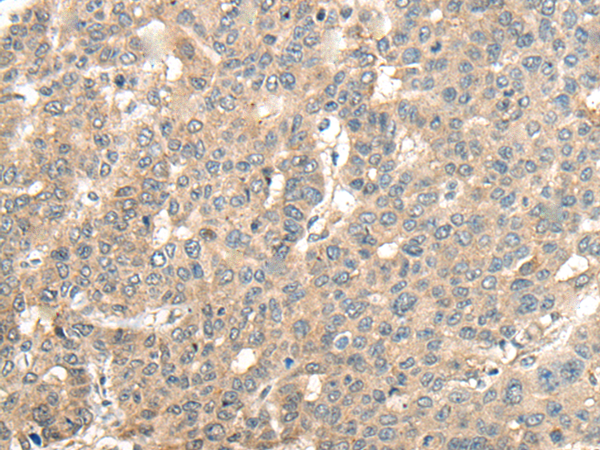
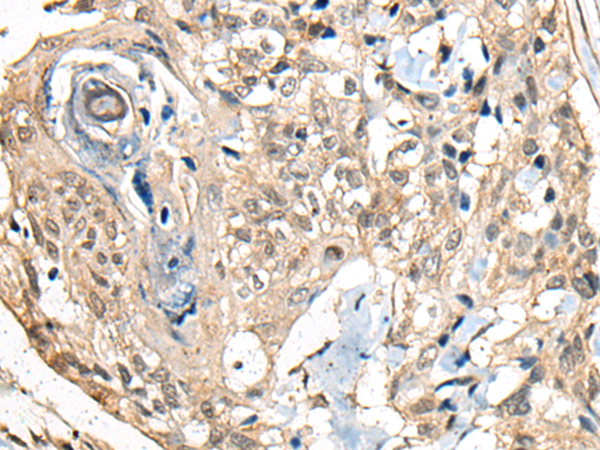
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GS; DP2; DP3; BTPS2; DP2.5; PPP1R46 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human APC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于APC(Adenomatous Polyposis Coli)蛋白抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其功能、突变及相关疾病的研究:
1. **文献名称**:*Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21*
**作者**:Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B 等
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆了APC基因,并证实其在家族性腺瘤性息肉病(FAP)和结直肠癌中的高频突变,揭示了APC作为肿瘤抑制因子的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*The canonical Wnt signaling pathway and its APC partner in colon cancer development*
**作者**:Clevers H
**摘要**:文章系统总结了APC蛋白通过调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制肿瘤的机制,并强调APC突变导致β-catenin异常积累,从而驱动结直肠癌的发生。
3. **文献名称**:*APC mutations in colorectal tumours: Importance of the position of the pathogenic mutation*
**作者**:Aoki K, Taketo MM
**摘要**:该研究分析了APC基因不同位点突变对蛋白功能的影响,指出突变位置与肠道肿瘤表型严重程度的相关性,为临床诊断提供了分子依据。
4. **文献名称**:*Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling*
**作者**:Polakis P
**摘要**:文献综述了APC蛋白在Wnt通路中的核心作用,阐明其通过降解β-catenin维持肠道上皮稳态,并讨论APC缺失如何引发细胞增殖失控及癌变。
---
注:若用户指“APC抗体”为抗原呈递细胞(Antigen-Presenting Cell)相关研究,请补充说明以便调整参考文献方向。
Antibodies targeting the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein are critical tools in cancer research and diagnostics. APC is a multifunctional tumor suppressor protein encoded by the *APC* gene, best known for its role in regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. By forming a destruction complex with other proteins like GSK-3β and Axin, APC promotes the degradation of β-catenin, preventing its nuclear translocation and subsequent activation of oncogenic genes. Mutations in the *APC* gene are strongly linked to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and sporadic colorectal cancers, often resulting in truncated, nonfunctional APC proteins that drive uncontrolled cell proliferation.
APC antibodies are widely used in research to study protein expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence. They help identify loss of APC function in tumors or detect truncated forms associated with pathogenic mutations. Clinically, APC antibodies aid in diagnosing hereditary cancer syndromes and understanding tumor progression. Recent studies also explore their potential in targeted therapies, such as stabilizing the APC-β-catenin interaction to restore pathway regulation. However, challenges remain in distinguishing between wild-type and mutant APC isoforms, necessitating antibody specificity validation. Overall, APC antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling APC’s complex roles in development and disease.
×