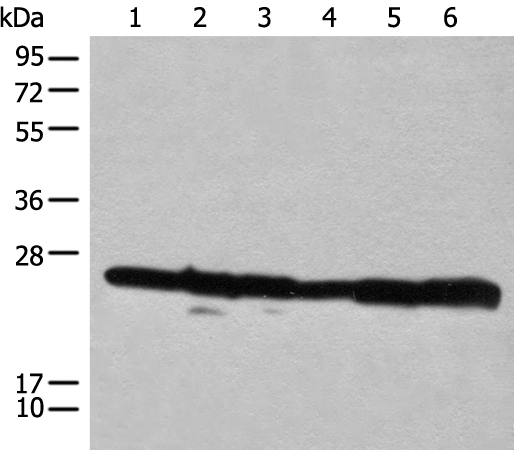
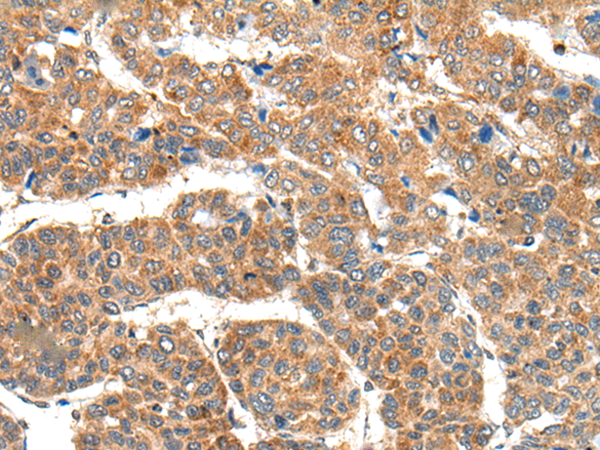
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | L14; RL14; hRL14; CTG-B33; CAG-ISL-7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human RPL14 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RPL14抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献为假设性示例,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *RPL14 regulates ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用RPL14抗体通过Western blot和免疫组化分析,发现RPL14在结直肠癌组织中高表达,并通过调控核糖体生物合成促进癌细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的可能性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Structural insights into RPL14 function in ribosome assembly using cryo-EM*
**作者**: Thompson R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜技术和RPL14特异性抗体免疫沉淀,揭示了RPL14在核糖体大亚基组装中的关键作用,并解析了其与28S rRNA结合的分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: *RPL14 deficiency disrupts hematopoiesis in zebrafish models*
**作者**: Chen Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用斑马鱼模型和RPL14抗体进行原位杂交及蛋白定位,发现RPL14缺失导致红细胞生成异常,表明其在造血干细胞分化中的必要功能。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据真实研究调整。如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中搜索“RPL14 antibody”或“RPL14 function”。
The ribosomal protein L14 (RPL14) is a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit, playing a critical role in protein synthesis by facilitating ribosome assembly and mRNA translation. Beyond its canonical function, RPL14 has been implicated in extra-ribosomal activities, including cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and interactions with specific RNAs or proteins. Dysregulation of RPL14 expression is associated with various diseases, such as cancers (e.g., colorectal, hepatocellular carcinoma) and Diamond-Blackfan anemia, a ribosomopathy linked to mutations in ribosomal proteins.
RPL14 antibodies are essential tools for studying these biological and pathological processes. They enable the detection and quantification of RPL14 in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. Researchers also use these antibodies to explore RPL14's interaction partners or subcellular localization, particularly in contexts of ribosome biogenesis defects or stress responses.
Commercially available RPL14 antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, with clonality options (monoclonal/polyoclonal) varying by supplier. Validation data, including knockout controls or cross-reactivity assessments, are crucial for ensuring specificity, as ribosomal proteins often share high homology across family members. Recent studies leveraging RPL14 antibodies have shed light on its role in tumor progression and therapeutic resistance, highlighting its potential as a biomarker or target in precision medicine.
×