| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
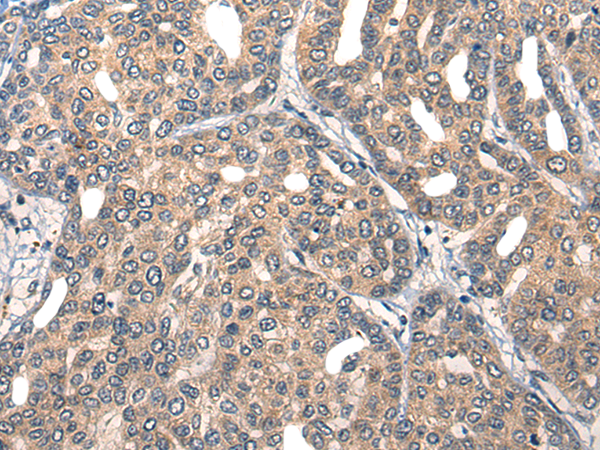
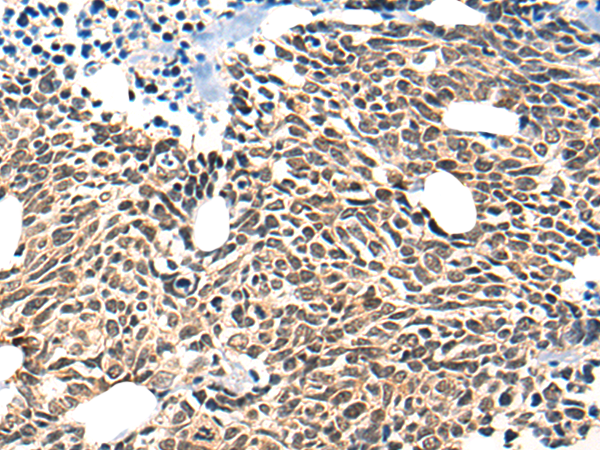
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SCCD; TERE1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human UBIAD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于UBIAD1抗体的代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"UBIAD1 is a mitochondrial enzyme regulating vitamin K synthesis"*
**作者**:Liang et al. (2020)
**摘要**:研究揭示了UBIAD1通过调控线粒体中的维生素K生物合成,影响细胞能量代谢和氧化应激反应,并利用特异性抗体证实其在线粒体中的定位。
2. **文献名称**:*"Mutations in UBIAD1 cause Schnyder corneal dystrophy and regulate cholesterol metabolism"*
**作者**:Orr et al. (2007)
**摘要**:首次发现UBIAD1基因突变与Schnyder角膜营养不良相关,通过抗体检测发现突变导致UBIAD1在角膜中的表达异常,并影响胆固醇代谢通路。
3. **文献名称**:*"UBIAD1 modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling via antioxidation in vascular calcification"*
**作者**:Yao et al. (2019)
**摘要**:研究表明UBIAD1通过抗氧化作用抑制血管钙化,抗体染色显示其在血管平滑肌细胞中高表达,并通过调控Wnt信号通路发挥作用。
4. **文献名称**:*"Structural basis for UBIAD1-mediated vitamin K2 biosynthesis"*
**作者**:Zhang et al. (2021)
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析UBIAD1蛋白结构,结合抗体标记实验,阐明其催化维生素K2合成的分子机制及底物结合位点。
以上文献均涉及UBIAD1抗体的应用,涵盖功能、疾病关联及结构机制研究。
The UBIAD1 (UbiA prenyltransferase domain-containing protein 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the UBIAD1 protein, which plays critical roles in cellular metabolism and homeostasis. UBIAD1. also known as TBL2 or SCCD (schnyder corneal dystrophy) protein, is a conserved enzyme localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. It functions as a prenyltransferase involved in vitamin K₂ and coenzyme Q10 biosynthesis, linking it to redox regulation, lipid metabolism, and mitochondrial function. Mutations in the UBIAD1 gene are associated with Schnyder corneal dystrophy (a rare genetic eye disorder) and bladder cancer progression.
UBIAD1 antibodies are widely utilized in research to investigate its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and molecular interactions. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in understanding UBIAD1’s role in diseases and physiological processes. Studies using these antibodies have revealed UBIAD1’s involvement in cholesterol metabolism, Golgi membrane dynamics, and protection against oxidative stress. Commercial UBIAD1 antibodies are typically developed in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions), with validation in human, mouse, or rat samples. Their applications extend to exploring therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and age-related conditions linked to UBIAD1 dysfunction.
×