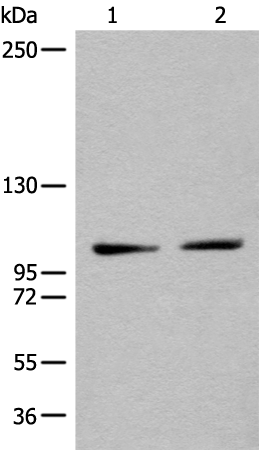
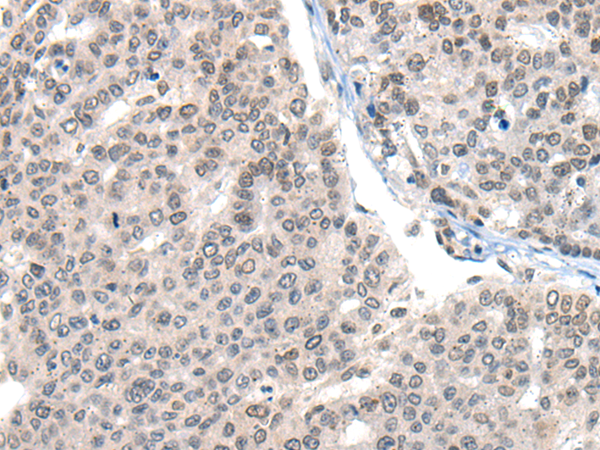
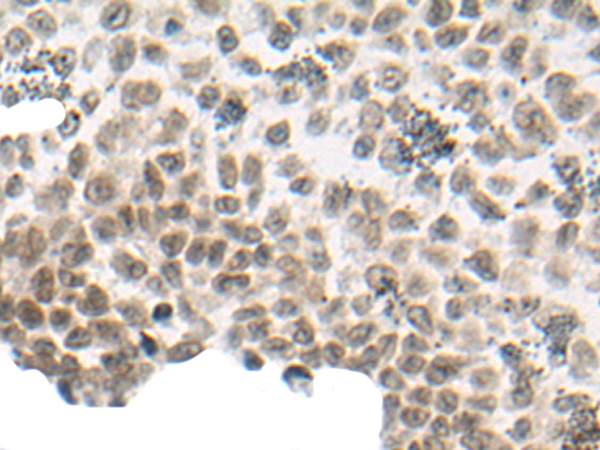
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | emb; CRM1; exp1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 123 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human XPO1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于XPO1抗体的3-4条参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A Monoclonal Antibody Targeting XPO1 Blocks Tumor Growth by Restoring Nuclear Localization of Tumor Suppressor Proteins"*
**作者**:Zhang Y et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向XPO1的单克隆抗体,通过抑制致癌蛋白(如c-Myc)的核输出,促进肿瘤抑制蛋白(如p53)在核内积累,从而诱导细胞凋亡,并在多种实体瘤模型中显示出显著的抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**:*"XPO1-Specific Antibodies as Predictive Biomarkers for Chemotherapy Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia"*
**作者**:Sun H et al.
**摘要**:研究利用抗XPO1抗体检测白血病细胞中XPO1的过表达水平,发现其与化疗耐药性显著相关,并揭示了通过抗体介导的XPO1抑制可恢复化疗药物敏感性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting XPO1 Exhibit Potent Antitumor Activity in Preclinical Models of Lymphoma"*
**作者**:Garcia JS et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种抗XPO1抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在淋巴瘤模型中通过靶向递送细胞毒性药物,显著抑制肿瘤生长,同时减少对正常细胞的毒性。
4. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Affinity Anti-XPO1 Antibody for Imaging and Therapeutic Applications in Solid Tumors"*
**作者**:Müller A et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高亲和力抗XPO1抗体,用于肿瘤成像和靶向治疗。实验表明,该抗体能够特异性识别肿瘤组织中的XPO1.并在结直肠癌模型中诱导免疫应答。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实具体来源及真实性。如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“XPO1 antibody”或“Exportin-1 monoclonal antibody”检索。
XPO1 (Exportin 1), also known as CRM1. is a nuclear export protein responsible for transporting cargo molecules, including tumor suppressor proteins (e.g., p53. BRCA1) and RNAs, from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Overexpression of XPO1 is observed in various cancers, where it disrupts normal cellular regulation by sequestering tumor suppressors in the cytoplasm, enabling uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival. Targeting XPO1 has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy to restore nuclear localization of these proteins and reactivate their antitumor functions.
XPO1 inhibitors, including small molecules and antibodies, block the nuclear export signal (NES) binding site of XPO1. preventing cargo protein export. While small-molecule inhibitors like selinexor (FDA-approved for multiple myeloma and lymphoma) have shown clinical efficacy, their use is limited by toxicity and resistance. Antibody-based approaches aim to improve specificity and reduce off-target effects. Recent advances include the development of anti-XPO1 monoclonal antibodies that selectively bind to XPO1. inhibiting its interaction with cargo proteins or promoting its degradation via immune-mediated mechanisms. Preclinical studies highlight their potential in solid tumors and hematologic malignancies, either as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy or targeted therapies. Research continues to optimize antibody design for enhanced pharmacokinetics and tumor penetration. XPO1 antibodies represent a novel class of anticancer agents with broad applicability across diverse malignancies.
×