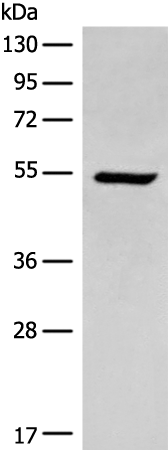
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PIP1; PTOP; TPP1; TINT1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ACD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于抗合成酶抗体(Antisynthetase Antibodies,ACD)的3篇代表性文献信息,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:《Clinical manifestations and outcomes of antisynthetase antibody-positive patients》
**作者**:Christopher-Stine L, et al.
**摘要**:该研究分析了抗合成酶抗体阳性患者的临床特征,发现间质性肺病(ILD)和肌炎是最常见表现,抗Jo-1抗体患者更易出现关节炎,而抗PL-7/PL-12抗体与ILD严重程度相关。
2. **文献名称**:《Antisynthetase syndrome: a review of the literature》
**作者**:Selva-O'Callaghan A, et al.
**摘要**:综述总结了抗合成酶综合征的病理机制及诊断标准,强调抗体的亚型(如抗Jo-1、PL-7、EJ等)与不同器官受累的相关性,并提出早期免疫抑制治疗可改善ILD预后。
3. **文献名称**:《Myositis-specific autoantibodies in interstitial lung disease: a prospective cohort study》
**作者**:Hozumi H, et al.
**摘要**:前瞻性队列研究表明,抗合成酶抗体阳性ILD患者肺功能下降更快,且对糖皮质激素联合免疫抑制剂治疗反应更敏感,提示抗体检测对ILD分层管理的重要性。
注:如需获取全文,建议通过PubMed或ResearchGate检索标题及作者信息。实际引用时请核对文献来源及发表年份。
×