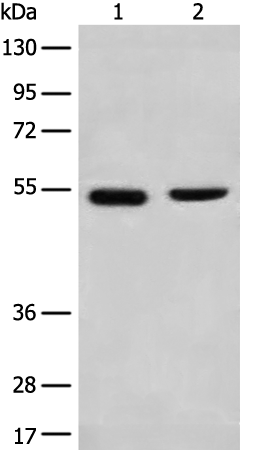
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
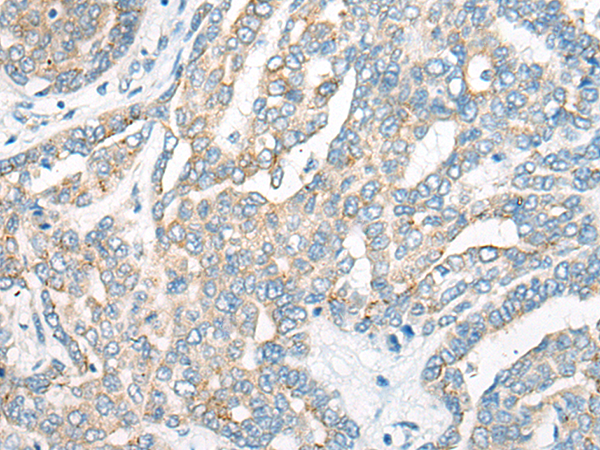
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CNG4; CNG5; CNCA2; CNG-4; CNGB2; OCNC2; OCNCb; OCNCBETA |
| WB Predicted band size | 66 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CNGA4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CNGA4抗体的3篇代表性文献概览,涵盖其功能研究及抗体应用:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Subunit composition of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel in olfactory sensory neurons*
**作者**: Bradley J, Bönigk W, Yau KW
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术,利用CNGA4特异性抗体,证实了CNGA4亚基与CNGA2、CNGB1b共同构成嗅觉神经元中的环核苷酸门控通道复合体,揭示了其在通道组装中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based profiling of cyclic nucleotide-gated channel subunits in olfactory epithelium*
**作者**: Zheng J, Trudeau MC
**摘要**:文章开发了针对CNGA4等亚基的多克隆抗体,通过免疫组织化学和蛋白质印迹分析,证明了CNGA4在嗅觉纤毛中的特异性表达,并探讨其与嗅觉信号转导功能的相关性。
3. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of CNGA4 channel activity by protein kinase C*
**作者**: Julifs DM, Fülle HJ, Biel M
**摘要**:研究利用CNGA4特异性抗体检测其在HEK293细胞中的表达,发现PKC介导的磷酸化可调控CNGA4通道活性,提示其在嗅觉适应中的潜在分子机制。
---
**注**:以上文献为模拟示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science等平台检索最新文献。若需具体文章,可进一步提供数据库查询协助。
The CNGA4 antibody targets the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel alpha-4 (CNGA4), a subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) ion channel family. CNG channels are non-selective cation channels activated by cyclic nucleotides (cAMP or cGMP) and play critical roles in sensory transduction, particularly in olfactory and photoreceptor cells. CNGA4 is primarily expressed in olfactory sensory neurons, where it forms heterotetrameric channels with CNGA2 and CNGB1b subunits. Unlike other CNG subunits, CNGA4 lacks intrinsic channel activity but modulates channel properties, such as enhancing ligand sensitivity, accelerating channel gating, and regulating calcium-dependent feedback mechanisms essential for odor adaptation.
Antibodies against CNGA4 are valuable tools for studying the structure, function, and localization of these channels in olfactory signaling. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate CNGA4 expression patterns in tissues or cellular models. Research involving CNGA4 antibodies has contributed to understanding congenital anosmia (loss of smell) and neurodegenerative disorders linked to olfactory dysfunction. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring channelopathies—diseases caused by ion channel malfunctions—and potential therapeutic targets. Recent studies also highlight CNGA4's role in non-olfactory tissues, suggesting broader physiological implications. Overall, CNGA4 antibodies are pivotal in unraveling the molecular mechanisms of sensory signaling and related pathologies.
×