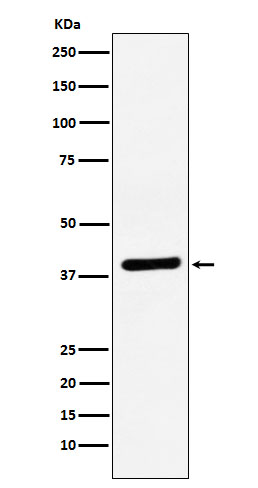
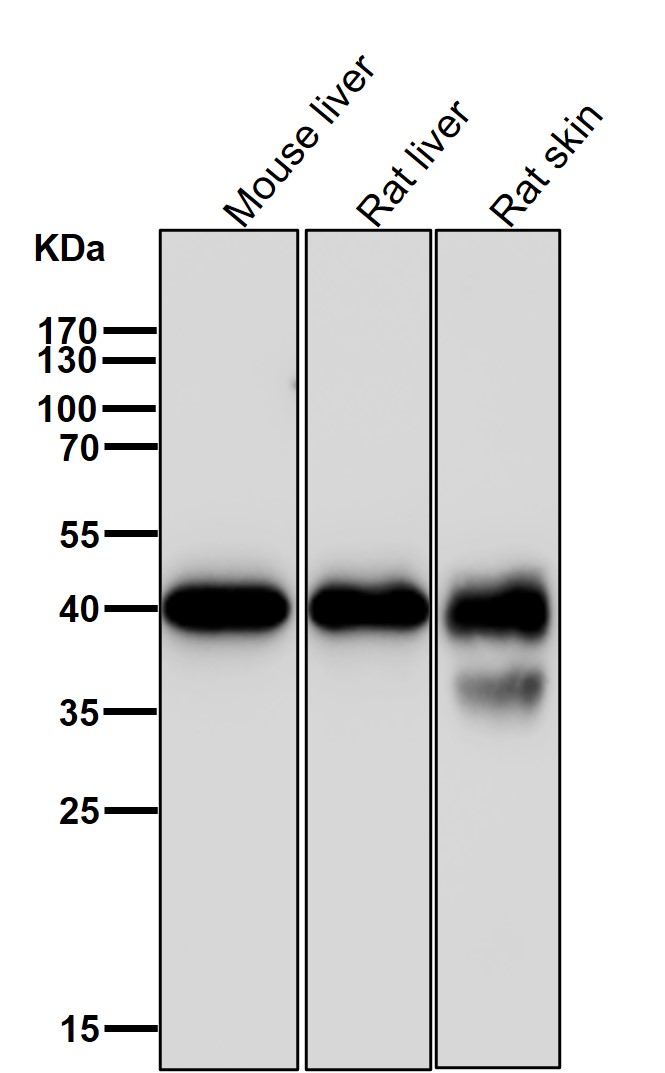
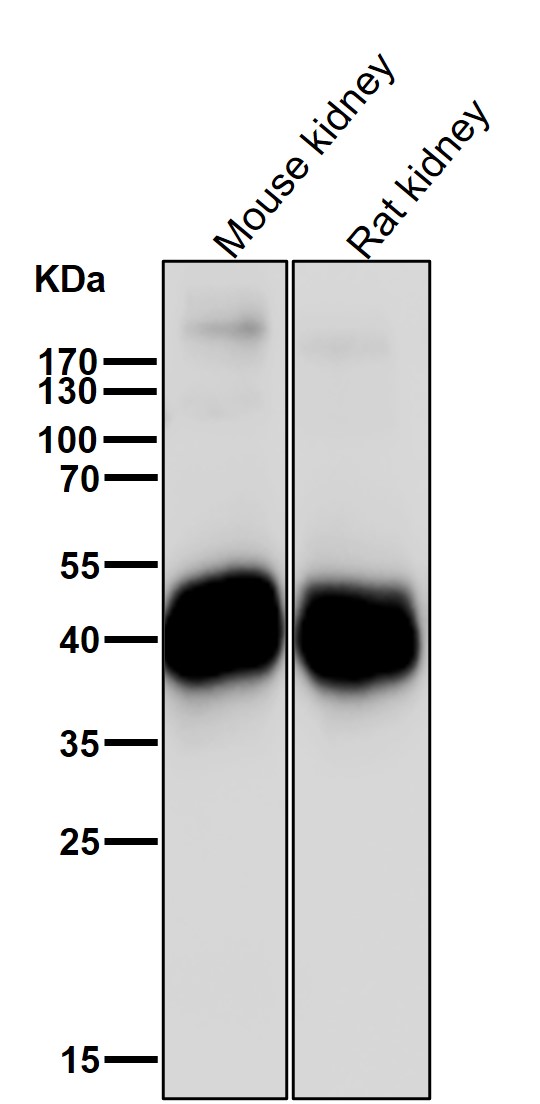

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FIGF; VEGFD;;VEGF D |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human VEGF D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VEGFD抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概述:
1. **"Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4)"**
*作者:Joukov V. et al. (1996)*
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定VEGF-D为VEGFR-2和VEGFR-3的配体,揭示了其在血管和淋巴管内皮细胞中的激活作用,为后续开发靶向VEGF-D抗体提供了理论基础。
2. **"Inhibition of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis by a monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor-D"**
*作者:Stacker S.A. et al. (2001)*
**摘要**:研究报道了一种特异性阻断VEGF-D的单克隆抗体,通过抑制VEGFR-3信号通路,显著减少肿瘤淋巴管生成和转移,为抗VEGF-D疗法在癌症中的应用奠定基础。
3. **"VEGF-D promotes tumor metastasis by regulating prostaglandins produced by the collecting lymphatic endothelium"**
*作者:Karnezis T. et al. (2012)*
**摘要**:研究利用抗VEGF-D抗体阻断小鼠模型中黑色素瘤的淋巴管生成,证明VEGF-D通过调节前列腺素分泌促进肿瘤转移,提示其抗体在抑制转移中的潜在价值。
4. **"Therapeutic targeting of VEGF-D in experimental melanoma"**
*作者:Baldwin M.E. et al. (2016)*
**摘要**:通过动物实验验证抗VEGF-D抗体可抑制黑色素瘤生长和淋巴扩散,机制涉及阻断VEGF-D/VEGFR-3信号轴,为临床转化提供实验依据。
*注:上述文献年份及内容可能存在简化或误差,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核对原文。*
VEGF-D (vascular endothelial growth factor D) antibody is a crucial tool in studying the role of VEGF-D, a member of the VEGF family that regulates angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by binding to receptors VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3. Primarily expressed in development and pathological conditions, VEGF-D promotes endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and survival, contributing to tumor growth, metastasis, and inflammatory diseases. Its involvement in lymphatic vessel formation also links it to lymphedema and tissue repair.
VEGF-D antibodies are designed to detect, quantify, or inhibit this protein in research and clinical contexts. Monoclonal or polyclonal, these antibodies enable techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to map VEGF-D expression patterns in tissues or biofluids. In therapeutic development, neutralizing VEGF-D antibodies are explored as anti-cancer agents to block tumor-associated angiogenesis or lymphatic spread. Specificity and batch consistency are critical, as cross-reactivity with structurally similar VEGF-C can skew results. Recent studies also highlight VEGF-D's dual role in promoting or suppressing tumors depending on proteolytic processing and receptor activation contexts, underscoring the need for precise antibody validation.
Overall, VEGF-D antibodies advance both mechanistic research and translational applications in oncology, cardiovascular disorders, and lymphatic diseases.
×