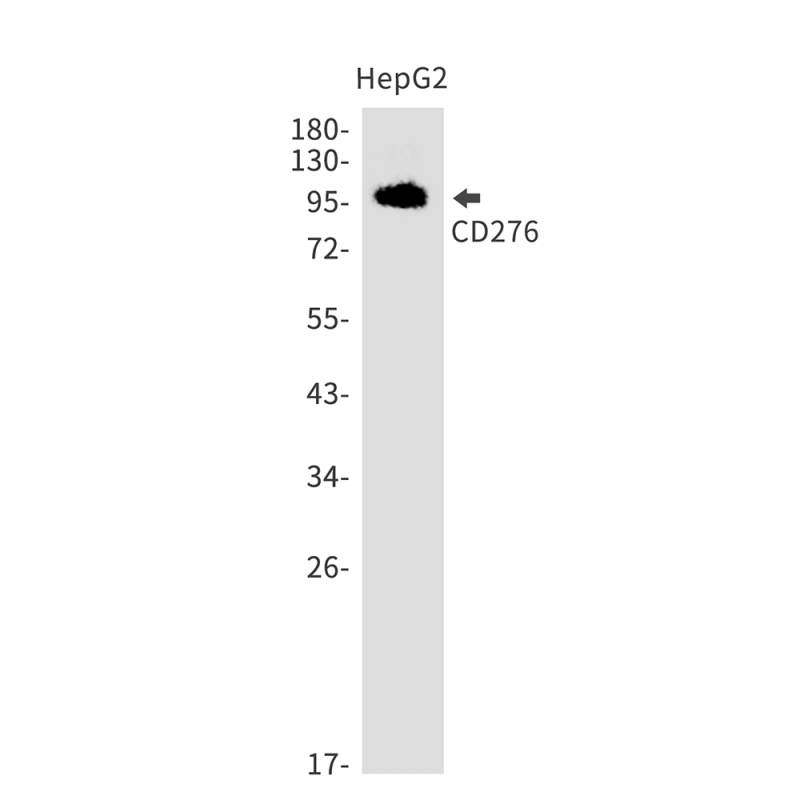
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7h3; B7RP-2; AU016588; 6030411F23Rik |
| Entrez GeneID | 102657 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 90-110 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse CD276 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD276抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*B7-H3: A Costimulatory Molecule for T Cell Regulation and Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**:Picarda E. 等(2016)
**摘要**:综述了CD276(B7-H3)的分子结构和免疫调节功能,指出其在多种肿瘤中异常高表达,并讨论其作为免疫治疗靶点的潜力,包括抗体药物和CAR-T疗法的开发方向。
---
2. **文献名称**:*An Anti-B7-H3 Antibody Inhibits Tumor Progression in Preclinical Models of Solid Tumors*
**作者**:Loo D. 等(2020)
**摘要**:报道了一种人源化抗CD276抗体的临床前研究,显示该抗体通过阻断免疫抑制信号并增强T细胞活性,显著抑制多种实体瘤(如肺癌、胰腺癌)的生长。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CD276 Antibody-Drug Conjugate for Targeted Breast Cancer Therapy*
**作者**:Seaman S. 等(2017)
**摘要**:开发了一种CD276靶向的抗体药物偶联物(ADC),在乳腺癌模型中通过特异性递送细胞毒性药物,显著缩小肿瘤体积,提示其在CD276高表达癌症中的治疗价值。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Dual Roles of B7-H3 in the Tumor Microenvironment*
**作者**:Castellanos J.R. 等(2017)
**摘要**:探讨CD276在肿瘤微环境中的双重作用,既可能通过抑制免疫细胞促进肿瘤进展,也可能被抗体靶向后激活抗肿瘤免疫反应,强调其作为治疗靶点的复杂性。
---
这些文献涵盖了CD276抗体的基础机制、药物开发及临床前研究,反映了其在肿瘤免疫治疗领域的多样性和潜力。
CD276. also known as B7-H3. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. Initially identified as a T-cell modulator, CD276 exhibits dual roles in immune activation and suppression, though its precise mechanisms remain under investigation. Structurally, it contains immunoglobulin-like (Ig) and variable (V) domains, with glycosylated regions influencing its interactions. While expressed at low levels in normal tissues, CD276 is frequently overexpressed in various cancers, including breast, lung, and prostate carcinomas, correlating with poor prognosis, metastasis, and immune evasion by dampening T-cell responses.
CD276-targeting antibodies have emerged as promising tools in cancer immunotherapy. These antibodies typically block CD276’s immune-inhibitory functions or deliver cytotoxic payloads via antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Preclinical studies highlight their potential to enhance anti-tumor immunity, inhibit angiogenesis, and directly induce cancer cell apoptosis. Several monoclonal antibodies (e.g., enoblituzumab) and CAR-T cell therapies targeting CD276 are in clinical trials, often combined with checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy.
Challenges include balancing efficacy with toxicity, as low CD276 expression in healthy tissues may still cause off-target effects. Additionally, tumor heterogeneity and resistance mechanisms necessitate further research. Despite these hurdles, CD276 antibodies represent a versatile strategy to exploit immune checkpoint pathways and tumor-specific antigens for precision oncology.
×