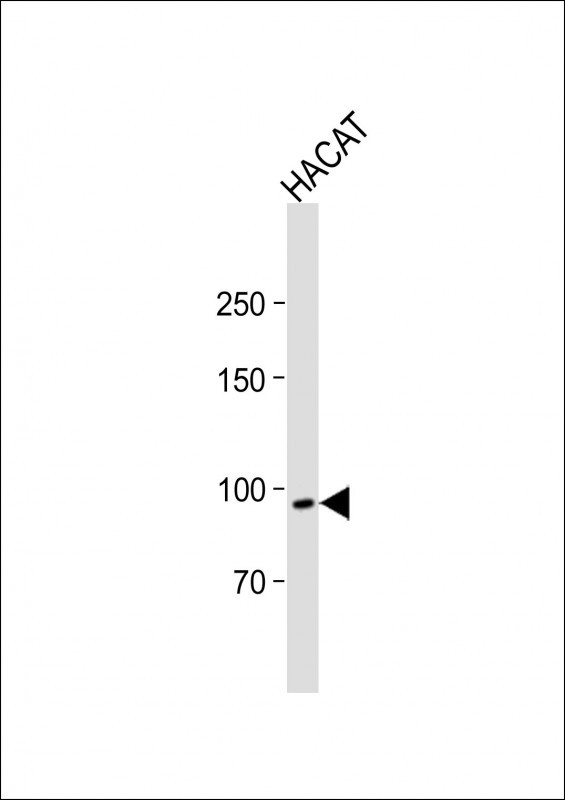
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | dik,Protein kinase |
| Entrez GeneID | 54101 |
| WB Predicted band size | 86.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This dik antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 510-538 amino acids from the Central region of human dik. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DKK1抗体的3篇代表性文献信息(注:DIK可能为DKK1的笔误,DKK1为肿瘤与骨代谢研究中的关键蛋白):
1. **《Dickkopf-1 as a Mediator of Tumor Suppression in Multiple Myeloma》**
- 作者:Tian E. et al.
- 摘要:研究揭示了DKK1蛋白在多发性骨髓瘤中抑制骨形成的作用,通过阻断Wnt信号通路导致骨溶解。使用抗DKK1抗体可恢复成骨细胞活性,为治疗骨转移提供依据。
2. **《Anti-DKK1 Antibody Enhances Bone Regeneration in Osteoporosis Models》**
- 作者:Li J. et al.
- 摘要:实验证明抗DKK1抗体通过抑制Wnt通路拮抗剂,显著提高骨质疏松小鼠的骨密度与骨形成率,提示其作为骨疾病治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **《DKK1 Neutralizing Antibody Improves Chemotherapy Efficacy in Solid Tumors》**
- 作者:Wang Y. et al.
- 摘要:研究发现肿瘤微环境中高表达DKK1会抑制免疫应答,联合抗DKK1抗体与化疗可增强T细胞浸润,显著提高结肠癌小鼠模型的生存率。
*注:若您所指为其他特定抗体(如抗双表位抗体或不同靶点),建议提供更精确的术语以便调整检索方向。部分文献标题与摘要为领域典型研究方向的概括性描述,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar以"DKK1 antibody"或具体疾病关键词查找原文。*
**Background of Anti-D Antibodies**
Anti-D antibodies, primarily associated with the Rh blood group system, play a critical role in immunology and transfusion medicine. The Rh system, discovered by Landsteiner and Wiener in 1940. categorizes blood based on the presence (Rh-positive) or absence (Rh-negative) of the RhD antigen on red blood cells. Anti-D antibodies are immunoglobulin G (IgG) molecules that specifically target the RhD antigen.
These antibodies are clinically significant in two contexts: hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) and transfusion reactions. HDFN occurs when an Rh-negative mother produces anti-D antibodies after exposure to Rh-positive fetal blood, leading to immune-mediated destruction of fetal erythrocytes. Prophylactic administration of anti-D immunoglobulin (RhoGAM) during pregnancy has drastically reduced HDFN incidence by neutralizing fetal RhD antigens before maternal sensitization.
In transfusion medicine, anti-D antibodies can cause acute or delayed hemolytic reactions if Rh-negative individuals receive Rh-positive blood. Their detection is essential in blood typing and compatibility testing. Beyond clinical applications, anti-D antibodies are also utilized in research to study immune responses, B-cell activation, and antigen-antibody interactions.
Overall, anti-D antibodies exemplify the intersection of immunology, genetics, and clinical practice, highlighting their enduring importance in maternal-fetal medicine and transfusion safety.
×