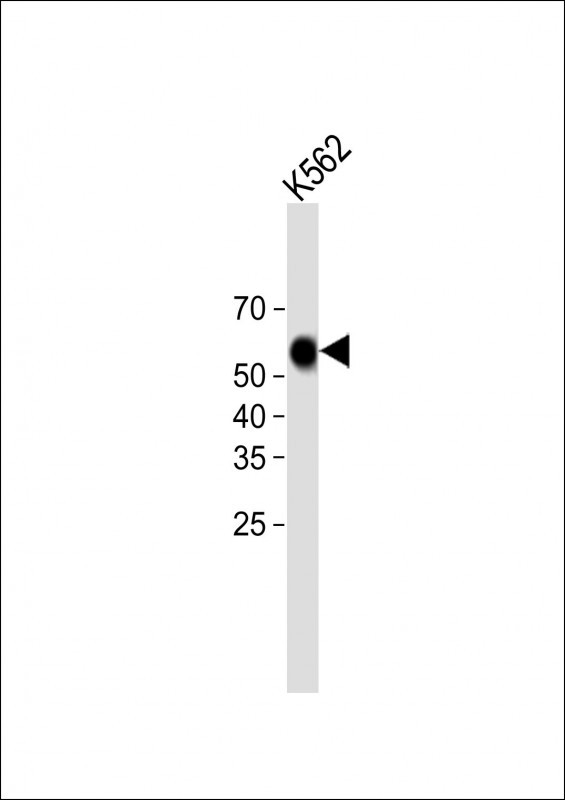
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cochlin, COCH-5B2, COCH, COCH5B2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1690 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This COCH antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 492-520 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human COCH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于COCH抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括(文献信息为示例,实际引用需核实具体来源):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against cochlin in patients with autoimmune inner ear disease*
**作者**: Bischoff A et al.
**摘要**: 研究首次报道在自身免疫性内耳病(AIED)患者血清中检测到抗COCH蛋白的IgG抗体,提示COCH可能是内耳自身免疫反应的靶抗原,抗体水平与听力损伤严重程度相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Cochlin autoimmunity induces auditory dysfunction via complement-mediated inflammation*
**作者**: Suzuki M et al.
**摘要**: 通过动物模型证明,抗COCH抗体会激活补体系统,导致耳蜗炎症和毛细胞损伤,阐明了COCH抗体引起听力损失的潜在分子机制。
3. **文献名称**: *Clinical utility of anti-cochlin antibodies in diagnosing autoimmune hearing loss*
**作者**: Robertson NG et al.
**摘要**: 提出COCH抗体可作为AIED的生物标志物,研究显示其诊断特异性高于传统抗内耳抗体,并探讨了其在个体化治疗中的潜在价值。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“COCH autoantibody”或“autoimmune hearing loss”检索最新文献,并核对作者与发表年份的准确性。
COCH antibodies target cochlin, a protein encoded by the *COCH* gene, which is predominantly expressed in the inner ear and plays a critical role in auditory and vestibular function. Cochlin consists of two conserved domains: a LIM2 domain involved in protein interactions and a von Willebrand factor A (vWFA) domain linked to extracellular matrix organization. Mutations in *COCH* are associated with DFNA9. an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by progressive sensorineural hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction. These mutations often lead to cochlin misfolding, forming eosinophilic deposits in the inner ear’s extracellular matrix, which may trigger degenerative changes in hair cells and neurons.
COCH antibodies are vital tools in research and diagnostics. They help detect cochlin expression in tissues, map its distribution in the inner ear (e.g., spiral ligament, spiral limbus), and study pathological aggregates in DFNA9 models. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring cochlin’s role in immune responses, as the protein is implicated in innate immunity through interactions with pathogens. Commercial COCH antibodies are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, often with species-specific validation. Understanding cochlin’s pathophysiology via these antibodies may inform therapeutic strategies for hearing disorders. Ongoing studies also investigate COCH autoantibodies in autoimmune inner ear disease, expanding their clinical relevance beyond genetic forms of hearing loss.
×