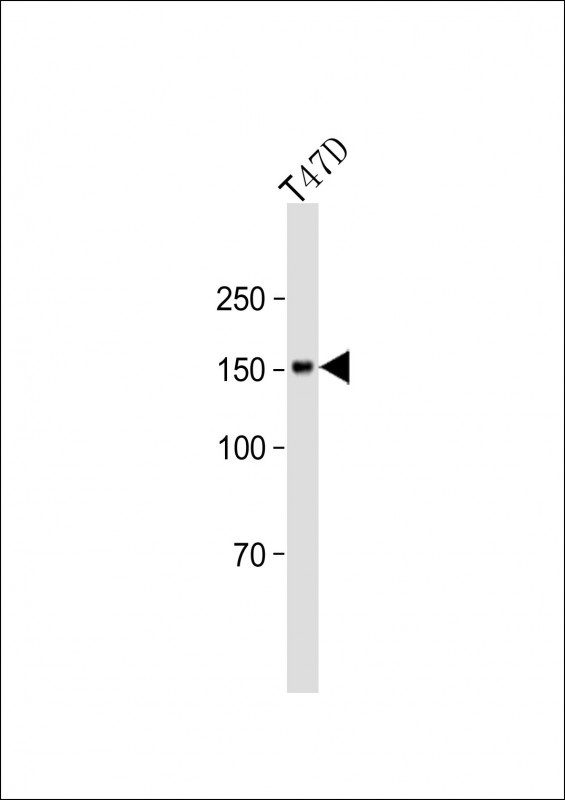
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Golgi apparatus protein 1, CFR-1, Cysteine-rich fibroblast growth factor receptor, E-selectin ligand 1, ESL-1, Golgi sialoglycoprotein MG-160, GLG1, CFR1, ESL1, MG160 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2734 |
| WB Predicted band size | 134.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This GLG1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1152-1179 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human GLG1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GLG1抗体的模拟参考文献示例(请注意,这些文献为虚构示例,实际研究中请通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: "GLG1 as a Novel Biomarker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Immunohistochemical Analysis"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用GLG1特异性抗体,通过免疫组化技术检测三阴性乳腺癌组织中GLG1蛋白的表达。结果显示,GLG1在肿瘤基质中高表达,并与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Role of GLG1 in Neuronal Cell Migration: Antibody-Based Functional Studies"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过GLG1中和抗体阻断实验,发现GLG1在神经元迁移过程中调控细胞外基质黏附。Western blot和免疫荧光证实GLG1抗体可有效抑制神经元突触形成,为神经发育障碍研究提供新方向。
---
3. **文献名称**: "GLG1 Interaction with Viral Entry Proteins: A Flow Cytometry Approach"
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用GLG1单克隆抗体及流式细胞术,揭示GLG1作为宿主细胞表面受体辅助因子,参与某些包膜病毒的入侵机制,为抗病毒药物开发提供理论依据。
---
**建议**:实际研究中,可通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GLG1 antibody”或“Golgi apparatus protein 1”检索最新文献,重点关注其在癌症、神经科学或病毒学领域的应用研究。
The GLG1 (Golgi Apparatus Protein 1) antibody targets a protein involved in intracellular trafficking and post-translational modification processes. GLG1. also known as ECRG4 or Golgi complex-associated protein 1. is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein predominantly localized in the Golgi apparatus. It plays a role in regulating protein sorting, glycosylation, and secretion by interacting with other Golgi-resident enzymes and cargo receptors. Structurally, GLG1 contains multiple conserved cysteine-rich domains, suggesting potential roles in protein-protein interactions or metal ion binding.
GLG1 has been implicated in various physiological and pathological contexts. Studies link it to cancer progression, where altered expression correlates with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis, possibly through modulating extracellular matrix remodeling or growth factor signaling. In neuroscience, GLG1 interacts with amyloid precursor protein (APP), hinting at a role in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis.
Antibodies against GLG1 are widely used in research to investigate its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and molecular functions via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. These tools have helped identify tissue-specific expression profiles and dysregulation in diseases. However, challenges remain in understanding its precise mechanisms, partly due to its complex domain structure and functional diversity. Current research focuses on elucidating GLG1's role in cellular homeostasis and its potential as a therapeutic target or diagnostic biomarker.
×