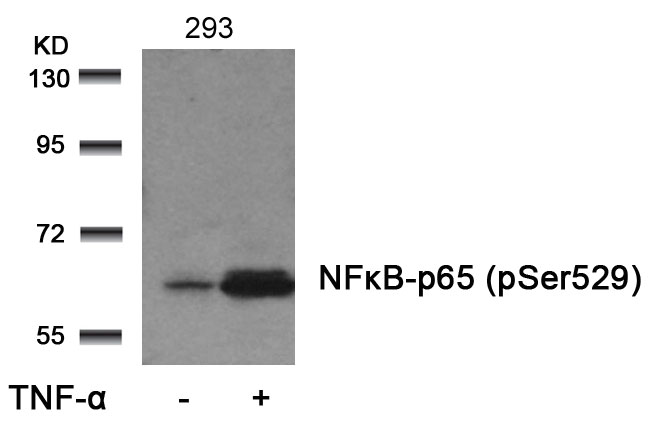


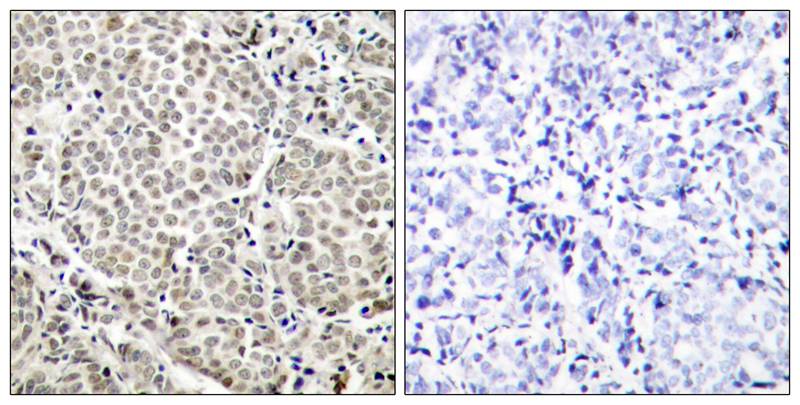
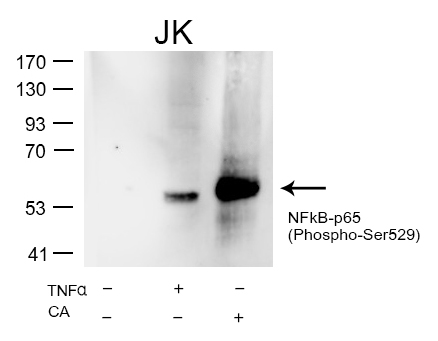
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFKB3; RELA; TF65; Transcription factor p65; p65 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5970; |
| WB Predicted band size | 65kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 529 (L-L-S(p)-G-D) derived from Human NFkB-p65. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Ser529)抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at Ser529 regulates transcriptional activation"**
- **作者**: Sakurai, H., et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 研究报道了T细胞受体(TCR)激活后,p65亚基Ser529位点的磷酸化通过IKK复合体调控,促进NF-κB转录活性;使用特异性抗体验证了该位点的磷酸化与炎症基因表达的相关性。
2. **"Site-specific phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 by protein kinase C regulates interleukin-6 expression"**
- **作者**: Deng, L., et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 发现IL-1刺激诱导p65 Ser529磷酸化,依赖PKCζ激酶;通过Phospho-Ser529抗体检测发现该修饰增强NF-κB与DNA结合能力,促进IL-6等细胞因子表达。
3. **"Differential regulation of NF-κB activation by phosphorylation of the p65 subunit"**
- **作者**: Barkett, M., & Gilmore, T.D. (1999)
- **摘要**: 比较多个p65磷酸化位点(包括Ser529)的功能,发现Ser529磷酸化通过抗体检测与核转位和抗凋亡基因激活相关,提示其在不同刺激下的特异性调控。
4. **"Regulation of NF-κB transcriptional activity by phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 529"**
- **作者**: Vanden Berghe, W., et al. (1998)
- **摘要**: 早期研究揭示TNF-α诱导的Ser529磷酸化通过抗体检测验证,并与p300/CBP共激活因子结合增强相关,进而驱动促炎基因表达。
这些文献均通过特异性抗体研究Ser529磷酸化在NF-κB通路中的分子机制及生物学意义。
The NF-κB-p65 (Phospho-Ser529) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of the NF-κB p65 subunit at serine residue 529. NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) is a transcription factor family critical for regulating immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and proliferation. The p65 subunit (RelA) is a key component of the canonical NF-κB pathway. In resting cells, NF-κB is sequestered in the cytoplasm by inhibitory IκB proteins. Upon activation by stimuli like cytokines, pathogens, or stress signals, IκB is degraded, allowing NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus and activate target genes.
Phosphorylation of p65 at specific serine residues, including Ser529. modulates its transcriptional activity, DNA binding affinity, and interactions with co-regulators. Ser529 phosphorylation is mediated by kinases such as casein kinase II (CK2) and contributes to the full transcriptional activation of NF-κB. This post-translational modification serves as a marker for NF-κB pathway activation in research contexts.
The NF-κB-p65 (Phospho-Ser529) antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study NF-κB activation dynamics in diseases involving chronic inflammation, cancer, or autoimmune disorders. It helps researchers assess pathway activity, correlate phosphorylation states with pathological conditions, and evaluate therapeutic interventions targeting NF-κB signaling. Specificity for the phosphorylated epitope ensures accurate detection of the activated form of p65.
×