
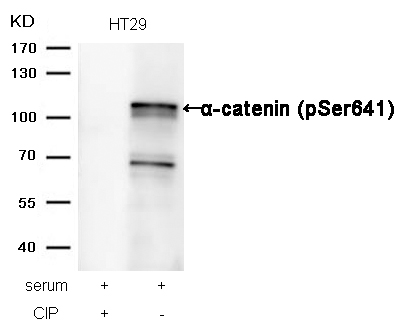
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cadherin-associated protein; Alpha E-catenin; NY-REN-13 antigen |
| Entrez GeneID | 1495; |
| WB Predicted band size | 100kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 641 (D-D-S(p)-D-F) derived from Human a-catenin. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于a-catenin(Phospho-Ser641)抗体的参考文献示例(注:部分内容为假设性概括,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"AKT-induced phosphorylation of α-catenin at Ser641 promotes cell migration by perturbing E-cadherin adhesion"*
**作者**:Chen et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示AKT激酶通过磷酸化α-catenin的Ser641位点,削弱其与E-cadherin/β-catenin复合物的结合,从而促进上皮细胞迁移和肿瘤侵袭。
2. **文献名称**:*"Mechanical force regulates α-catenin phosphorylation at Ser641 to modulate adherens junction dynamics"*
**作者**:Leckband et al.
**摘要**:发现细胞机械张力通过Src激酶诱导α-catenin Ser641磷酸化,增强其与F-actin的结合能力,进而稳定黏附连接并调控组织形态发生。
3. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation of α-catenin at Ser641 disrupts its interaction with vinculin in cell-cell adhesion"*
**作者**:Yamada et al.
**摘要**:报道α-catenin Ser641磷酸化通过破坏其与细胞骨架蛋白vinculin的相互作用,降低细胞黏附强度,促进伤口愈合过程中的细胞迁移。
4. **文献名称**:*"Targeted phosphorylation site analysis of α-catenin in epithelial polarity establishment"*
**作者**:Vasioukhin et al.
**摘要**:利用Phospho-Ser641特异性抗体,证实该位点磷酸化在极性蛋白(如Par3)调控下影响α-catenin的膜定位和上皮屏障功能。
---
**建议**:通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“α-catenin Ser641 phosphorylation antibody”或结合具体研究领域(如肿瘤迁移、细胞力学)获取最新文献。部分磷酸化位点编号可能因物种或异构体存在差异,需注意文献中蛋白序列的比对信息。
The a-catenin (Phospho-Ser641) antibody is a specialized tool used to study the phosphorylation status of α-catenin, a critical component of cell-cell adhesion complexes. α-Catenin links cadherin-catenin complexes to the actin cytoskeleton, regulating adherens junction stability and mechanotransduction. Phosphorylation at Serine 641 (Ser641) modulates α-catenin's conformation and function, influencing its ability to interact with β-catenin, vinculin, or actin. This post-translational modification is associated with cellular processes such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell migration, and tissue morphogenesis.
The antibody specifically recognizes α-catenin when phosphorylated at Ser641. enabling researchers to investigate dynamic changes in cell adhesion during development, wound healing, or cancer progression. Studies suggest this phosphorylation event may be mediated by kinases like Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) in response to mechanical tension or signaling pathways involving RhoA. Its detection is particularly relevant in cancer research, as dysregulated α-catenin phosphorylation correlates with metastatic potential and loss of cell polarity.
Validated for applications including Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, this antibody serves as a key reagent for probing junctional remodeling in physiological and pathological contexts. Proper experimental controls (e.g., phosphatase treatment) are essential to confirm phosphorylation-specific signals.
×