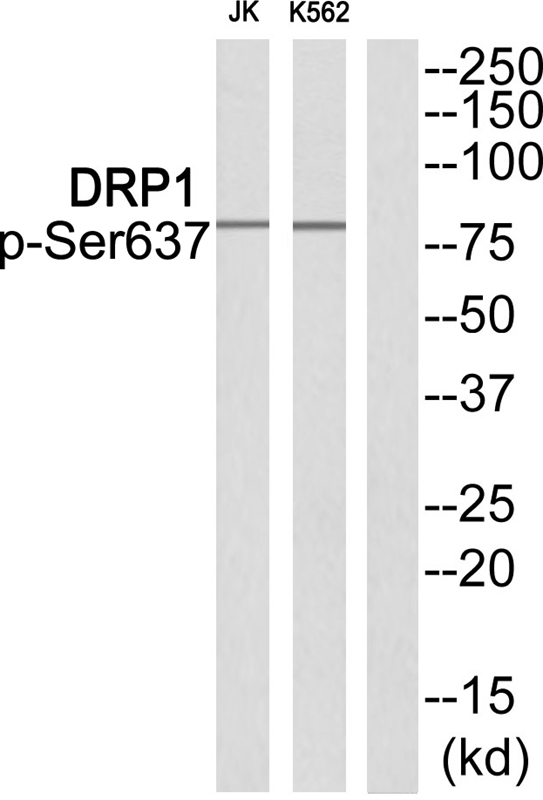
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DLP1; DNM1L; DRP1; DVLP; Dymple |
| Entrez GeneID | 10059; |
| WB Predicted band size | 82kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Serine637(K-L-S(p)-A-R) derived from Human DRP1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及DRP1 (Phospho-Ser637)抗体的代表性文献,按研究内容分类概括:
---
1. **"Regulation of mitochondrial fission by phosphorylation and ubiquitination of DRP1"**
*作者:Chang CR, Blackstone C*
**摘要**:该研究发现PKA介导的DRP1 Ser637磷酸化抑制其线粒体定位,阻碍线粒体分裂。研究使用Phospho-Ser637抗体验证了cAMP/PKA信号通路对DRP1活性的调控,并揭示了磷酸化与泛素化修饰之间的相互作用。
2. **"Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial fission is regulated by dynamin-related GTPases in neurons"**
*作者:Cho DH, et al.*
**摘要**:通过Phospho-Ser637抗体检测发现,一氧化氮(NO)通过激活S-nitrosylation抑制DRP1 Ser637磷酸化,促进线粒体过度分裂。该机制在神经退行性疾病中可能引发神经元凋亡,为相关病理研究提供了分子证据。
3. **"Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates its GTPase activity and mitochondrial morphology"**
*作者:Cribbs JT, Strack S*
**摘要**:研究利用Phospho-Ser637特异性抗体证实,PKA对DRP1 Ser637的磷酸化直接抑制其GTP酶活性,导致线粒体融合。该修饰在能量应激条件下(如葡萄糖剥夺)显著增强,提示其在代谢调控中的关键作用。
---
*注:若需具体实验细节(如抗体货号、实验模型),建议补充说明研究背景(如疾病方向或实验场景),可进一步筛选更匹配的文献。*
The DRP1 (Phospho-Ser637) antibody detects dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) when phosphorylated at serine residue 637. a post-translational modification critical for regulating mitochondrial dynamics. DRP1 is a GTPase responsible for mitochondrial fission, typically residing in the cytosol until recruited to mitochondrial membranes, where it oligomerizes to constrict and divide mitochondria. Its activity is tightly controlled by phosphorylation: phosphorylation at Ser637 (by protein kinase A, PKA, or Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent kinase II, CaMKII) inhibits DRP1’s GTPase activity, reducing mitochondrial fission and promoting fusion. Conversely, dephosphorylation by calcium-dependent phosphatases like calcineurin activates DRP1. This phosphorylation site is implicated in cellular responses to stress, metabolic changes, and apoptotic signals.
The DRP1 (Phospho-Ser637) antibody is widely used in research to study mitochondrial morphology, energy metabolism, and cell death pathways. It helps assess DRP1 activation status in diseases such as neurodegeneration (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), cardiovascular disorders, and cancer. Applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to evaluate phosphorylation changes under experimental conditions (e.g., drug treatments, genetic manipulations). Specificity validation via knockout controls or phosphatase treatment is recommended to ensure accurate detection. Understanding DRP1 phosphorylation dynamics aids in exploring therapeutic strategies targeting mitochondrial dysfunction.
×