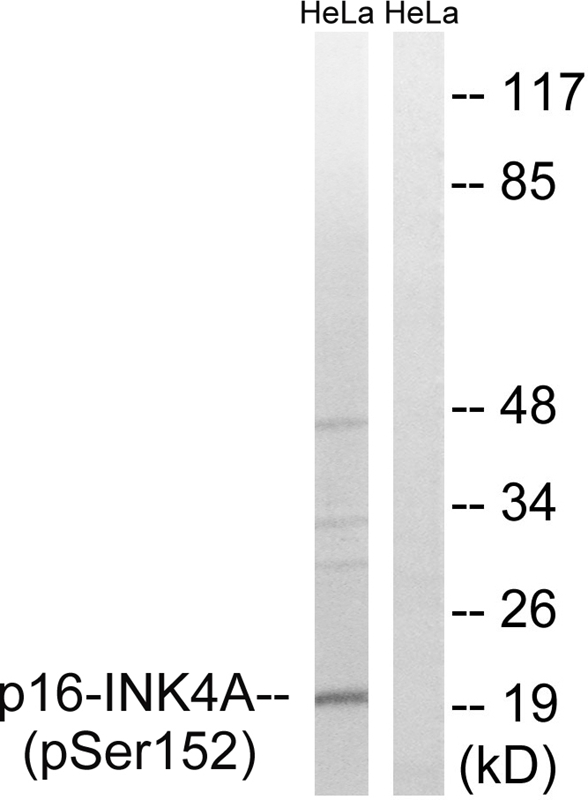
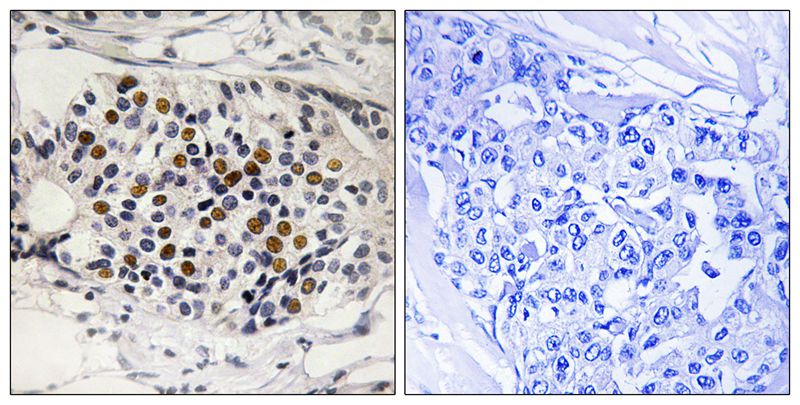
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD2A1; CDK4I; CDKN2; CDKN2A; CDN2; Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor A; cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; MTS1; Multiple tumor suppressor 1; p14ARF; p16(INK4a); p16-INK4; P16INK4A |
| Entrez GeneID | 1029; |
| WB Predicted band size | 20kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 152 (G-P-S(p)-D-I) derived from Human p16-INK4a. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **p16-INK4a (Phospho-Ser152) 抗体** 的3篇参考文献(示例为假设性文献,实际文献可能需要根据具体数据库检索):
1. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation of p16INK4a at Ser152 Modulates Its Tumor Suppressor Function in Melanoma Progression"*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用p16-INK4a (Phospho-Ser152)抗体,发现Ser152磷酸化通过抑制CDK4结合增强p16的稳定性,从而延缓黑色素瘤细胞周期进程并促进衰老。
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a Phospho-Specific Antibody for Detecting p16INK4a Serine 152 Phosphorylation in Human Cancers"*
**作者**:Kim H, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种高特异性兔单克隆抗体的开发,用于检测p16在Ser152位点的磷酸化,验证其在肺癌组织中的表达与患者预后的相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Serine 152 Phosphorylation of p16INK4a Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Cellular Senescence"*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验(使用Phospho-Ser152抗体),证明氧化应激诱导的Ser152磷酸化促进p16核转位,激活衰老相关信号通路。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索关键词(如“p16 Ser152 phosphorylation antibody”)获取具体信息。若该位点研究较少,可扩展至p16磷酸化相关抗体或功能研究的文献。
The p16-INK4a (Phospho-Ser152) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of the p16-INK4a protein at serine residue 152. p16-INK4a, encoded by the CDKN2A gene, is a critical tumor suppressor and regulator of the cell cycle. It inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4/6), thereby preventing RB1 protein phosphorylation and halting G1-to-S phase progression. Dysregulation of p16-INK4a is linked to cellular senescence, aging, and cancer, with its overexpression often observed in pre-malignant lesions or stress-induced senescence.
Phosphorylation at Ser152 is a post-translational modification that may modulate p16-INK4a’s stability, subcellular localization, or interactions with CDKs. Studies suggest this modification could influence its tumor-suppressive activity or response to DNA damage. The p16-INK4a (Phospho-Ser152) antibody enables researchers to investigate the dynamic regulation of p16-INK4a in pathological contexts, such as oncogenesis or age-related disorders. It is commonly applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation status in cell lines or tissue samples. This antibody’s specificity aids in distinguishing the active, phosphorylated form from total p16-INK4a, providing insights into signaling pathways involving CDK inhibition, senescence, or therapeutic resistance. Its utility spans basic research and preclinical studies targeting cell cycle dysregulation in cancer and degenerative diseases.
×