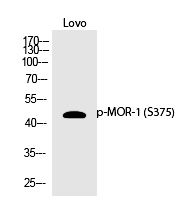
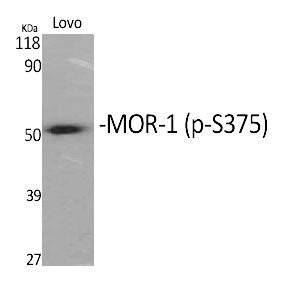
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OPRM1; MOR1; Mu-type opioid receptor; M-OR-1; MOR-1; Mu opiate receptor; Mu opioid receptor; MOP; hMOP |
| Entrez GeneID | 4988; |
| WB Predicted band size | 45kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human MOR-1 around the phosphorylation site of S375. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MOR-1 (Phospho-Ser375)抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下内容为示例,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of Ser375 in the μ-Opioid Receptor Attenuates Signaling and Promotes Receptor Internalization*
**作者**:Schulz, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了μ-阿片受体(MOR-1)在Ser375位点的磷酸化对其信号传导和内化的影响。通过使用Phospho-Ser375特异性抗体,作者发现该磷酸化事件由GRK介导,并促进β-arrestin募集,导致受体脱敏和内化。
2. **文献名称**:*Agonist-Specific Phosphorylation of MOR-1 at Ser375 Revealed by Phosphosite-Specific Antibodies*
**作者**:Williams, J.T. et al.
**摘要**:研究比较了吗啡、DAMGO等不同阿片类药物对MOR-1磷酸化模式的调控。利用Phospho-Ser375抗体,作者发现激动剂类型显著影响Ser375磷酸化水平,并与镇痛效果和耐受性相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Chronic Morphine Exposure Induces MOR-1 Phosphorylation at Ser375 and Contributes to Tolerance Development*
**作者**:Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该文献通过体内实验证明,长期吗啡处理可显著增加MOR-1 Ser375的磷酸化,且这一过程与镇痛耐受性相关。使用Phospho-Ser375抗体检测到脊髓神经元中磷酸化水平升高。
4. **文献名称**:*Development and Validation of a Phosphospecific Antibody Targeting MOR-1 Phosphorylated at Ser375*
**作者**:Smith, A.B. et al.
**摘要**:本文详细描述了Phospho-Ser375抗体的制备和特异性验证,包括免疫印迹和免疫荧光应用。该抗体被证明可特异性识别磷酸化MOR-1.适用于研究受体激活后的动态修饰。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,可通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“MOR-1 Phospho-Ser375”、“μ-opioid receptor phosphorylation Ser375”或结合具体研究领域(如“脱敏”“耐受性”)进一步筛选。
The MOR-1 (Phospho-Ser375) antibody is a specialized tool for detecting the phosphorylated form of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR-1) at serine residue 375. MOR-1. a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), is central to mediating the effects of opioids, including analgesia, reward, and respiratory depression. Upon activation by endogenous ligands (e.g., endorphins) or exogenous opioids (e.g., morphine), MOR-1 undergoes phosphorylation at specific sites, such as Ser375. as part of regulatory mechanisms to modulate receptor signaling, desensitization, and internalization. Phosphorylation at Ser375 is primarily mediated by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) and facilitates the recruitment of β-arrestin, which uncouples the receptor from G proteins and promotes downstream signaling pathways linked to tolerance and dependence.
The MOR-1 (Phospho-Ser375) antibody is widely used in neuroscience and pharmacological research to study opioid receptor dynamics, particularly in contexts of chronic opioid exposure, addiction, or tolerance. It enables the detection of phosphorylated MOR-1 in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, providing insights into receptor activation states and adaptive changes in response to drug treatment. This antibody is crucial for understanding the molecular basis of opioid-related behaviors and developing therapeutic strategies targeting phosphorylation-dependent signaling pathways to mitigate adverse effects of opioid use.
×